Recoding Data Model Fields (CX)
About Recoding Data Model Fields
Recoding allows you to change how data looks or behaves in CX Dashboards – for example, by conveniently shortening how choices are labeled, and changing text to numbers. You can only recode text set, multi-answer text set, and number set data.
This page covers how fields are recoded in the data modeler. For recoding dashboard fields in the older data mapper, see Recoding Dashboard Fields.
Source Recodes and Dashboard Recodes
In a data model dataset, source recodes are brought in. This means that if you recode a survey, then bring that survey into your data model, your survey recodes exist. When you recode the dashboard dataset, you are making changes to already recoded data.
Example: We have a survey with a satisfaction question with the following ratings and recodes:
- Very satisfied – 1
- Satisfied – 2
- Neither satisfied nor unsatisfied – 3
- Dissatisfied – 4
- Very dissatisfied – 5
In the survey, we edit the recodes as follows:
- Very satisfied – 5
- Satisfied – 4
- Neither satisfied nor unsatisfied – 3
- Dissatisfied – 2
- Very dissatisfied – 1
This second set of recode values is what we’ll see when we edit recode values in the dashboard. That also means that if we wanted to change “Very dissatisfied” to equal 0, we should recode the value of 1, not 5.
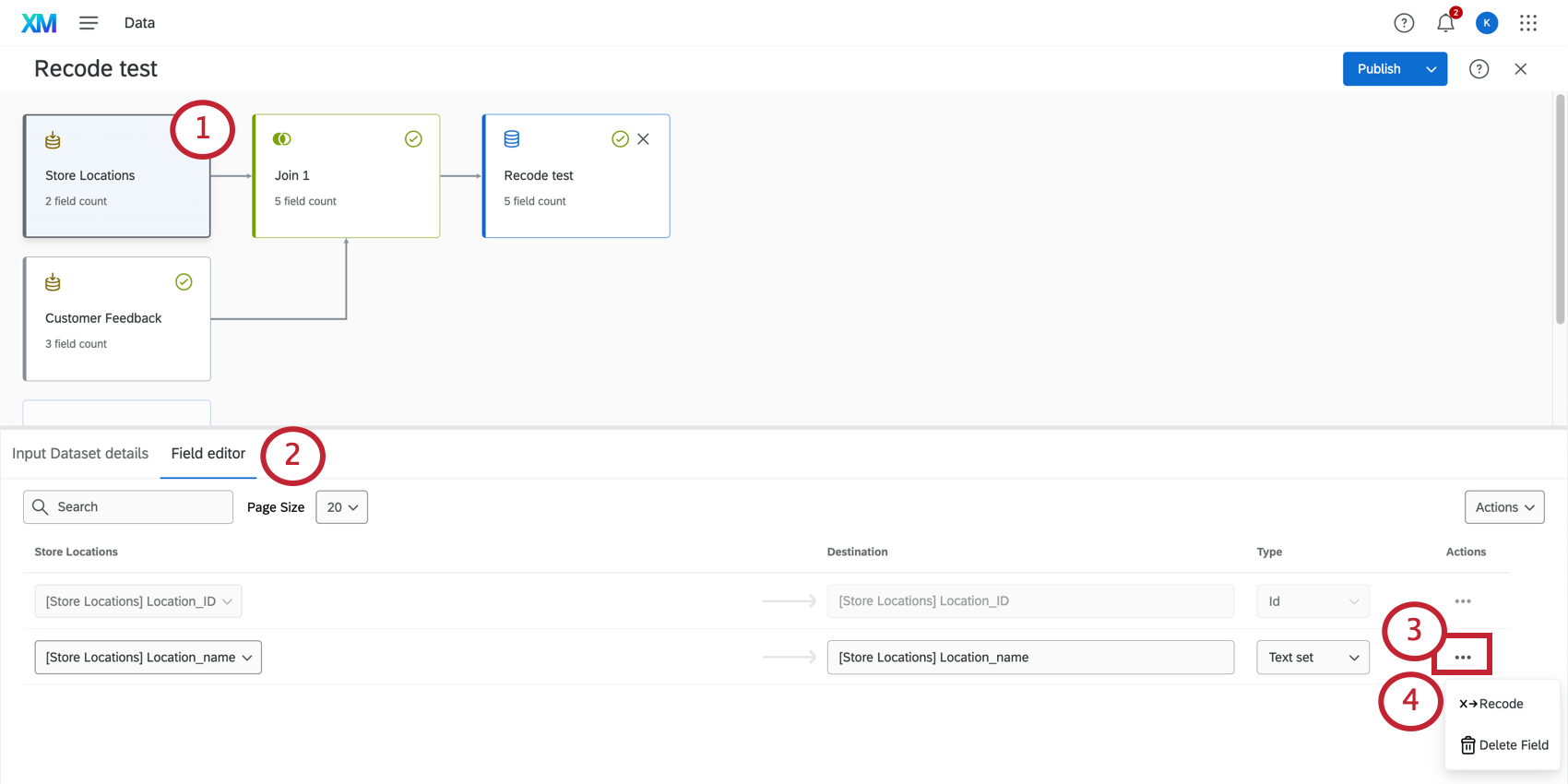
Opening the Recode Editor
You can only recode values at the source in a data model. These recode values are then carried through the model’s joins, unions, and output dataset.
- Select the source you want to recode.
- Select Field editor.
- Click the Actions button next to a text set, multi-answer text set, or number set field.
- Select Recode.
The recode editor will vary based on the format of your field.
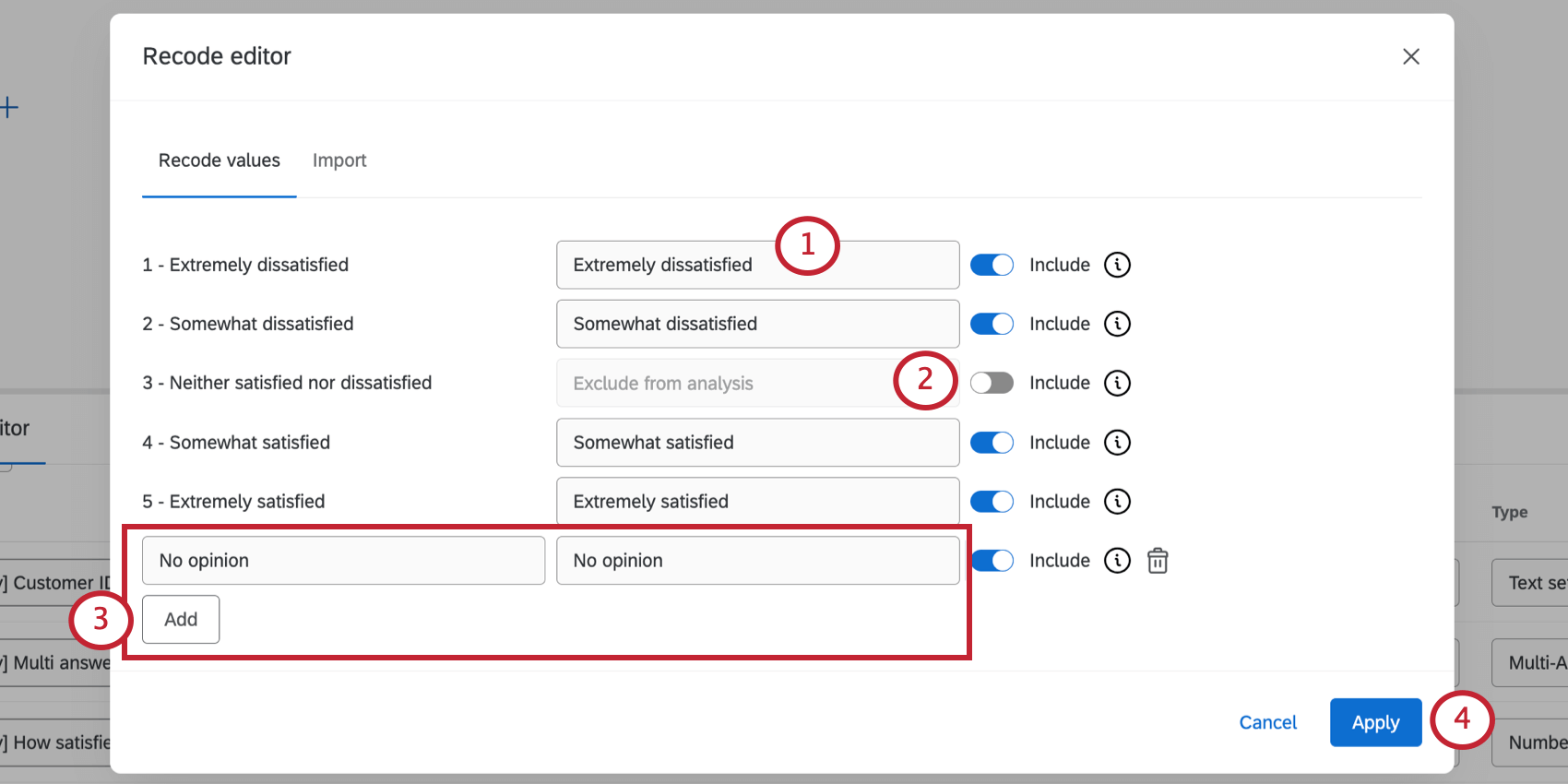
Recoding Fields
- For each value, you can change the spelling and wording. This is how the option will then appear in the dashboard.
Qtip: Note that the recode values are limited by field type. For example, if you want to recode NPS scores to NPS groups, the field type must be text set instead of a number set because the recoded values will be text instead of numbers.
- To exclude a value from analysis, select Include. Once this is grayed out, this value will be replaced with null values.
Qtip: If an option is excluded from analysis, it will be hidden and ignored in the dashboard. For example, marking a field as excluded from analysis will remove the field from metric calculations, dashboard exports, widgets, etc.
- If you want to add another value, click Add and fill out the fields.
Qtip: You can delete this value by clicking the trash icon.
- When you’re finished, click Apply.
You do not have to add options and recode values if you don’t want to. Data doesn’t have to be recoded to appear in the dashboard; the recode editor just allows you to format the way it will be labeled in your widgets.
For example, If you asked respondents to tell you what type of jewelry they have, they might give answers like “gold” or “silver.” By recoding values, you can align how similar options appear. See Cleaning Up Data.
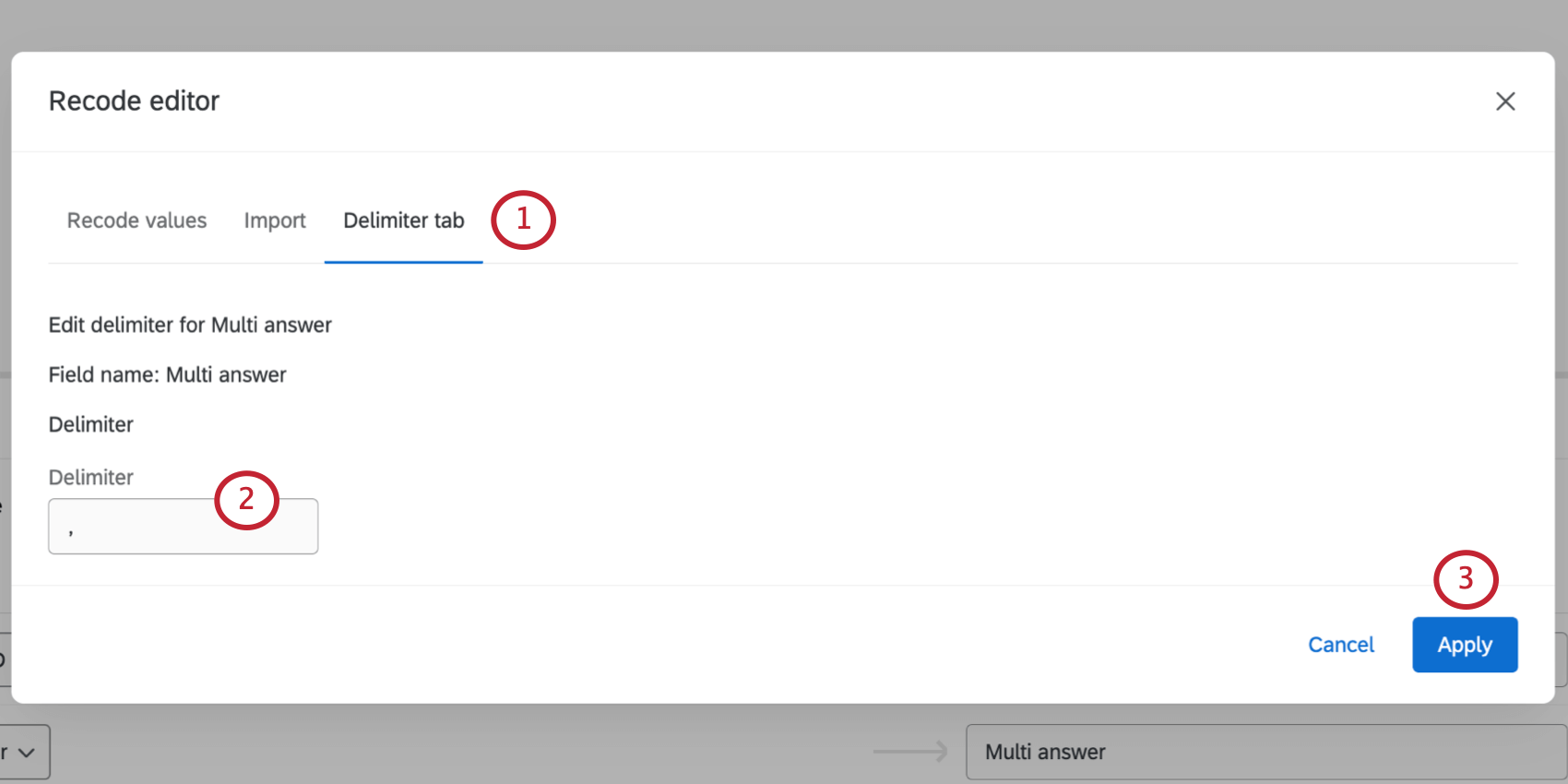
Managing Delimiters
When you’re mapping an open-ended field (such as a text entry question or an embedded data field) to a multi-answer text set, you have the option to define a delimiter. A delimiter determines the division between different answers entered into an open-ended field. For example, if you asked respondents to list the names of their children separated by commas, then the delimiter would be a comma.
- In the recode editor, go to Delimiter tab.
- Type your Delimiter in the field.
- Click Apply.
Importing Recode Values
You can also import recode values into your mapped fields. This is useful if you have many values you’d like to recode, or if you’re recoding the same field across multiple data sources.
- Go to the Import tab.
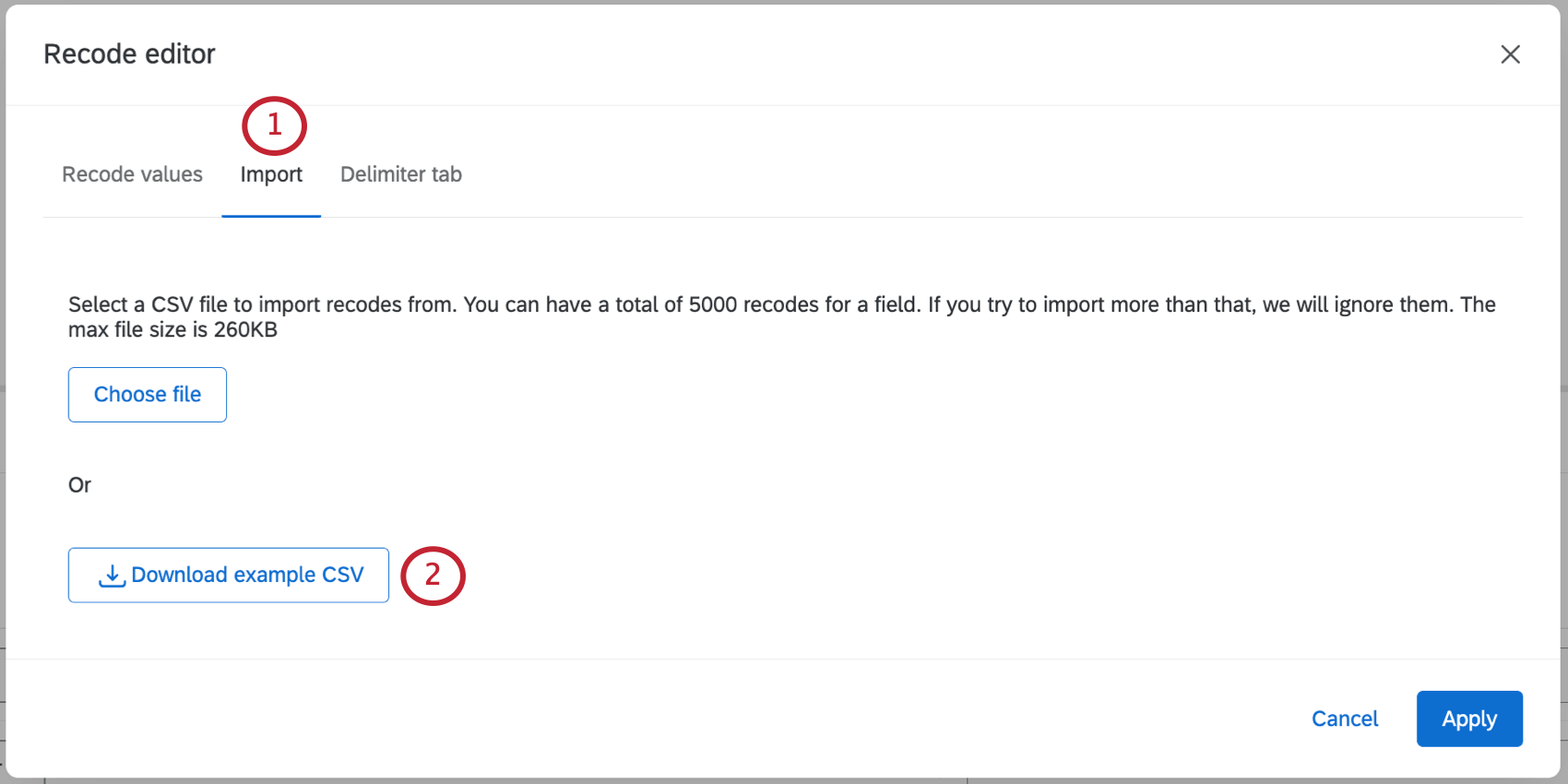
- Click Download example CSV. This file contains the current recode values for your field.
- Open the CSV file on your computer and define your recode values.
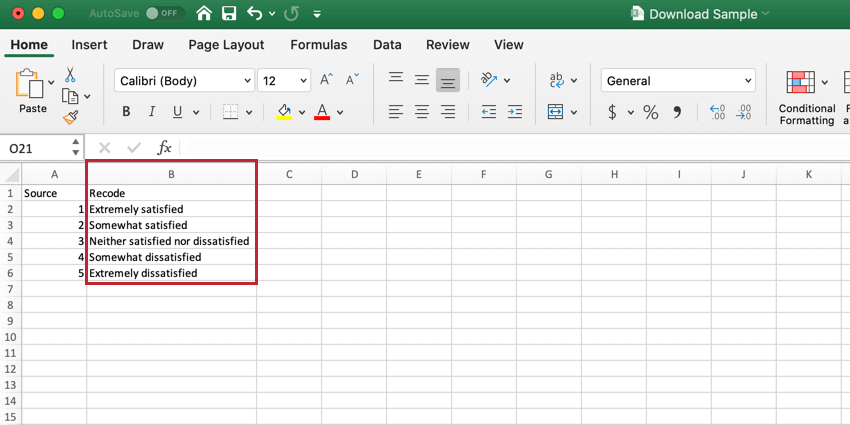 Qtip: If you leave a recode value blank, the answer choice will be excluded from analysis.
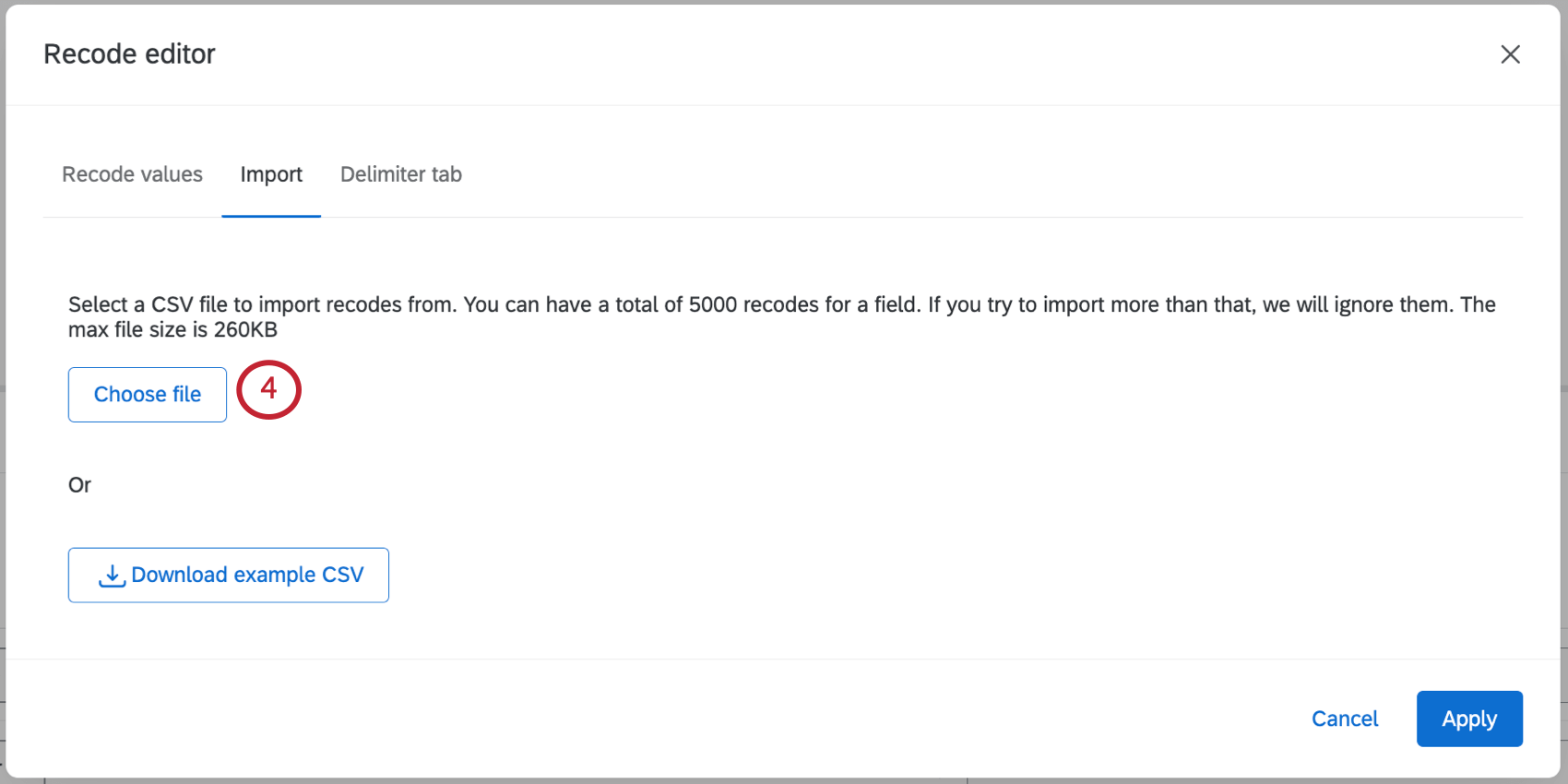
Qtip: If you leave a recode value blank, the answer choice will be excluded from analysis. - Click Choose file.
- If you’d like, you can double-check or edit the resulting recode values.
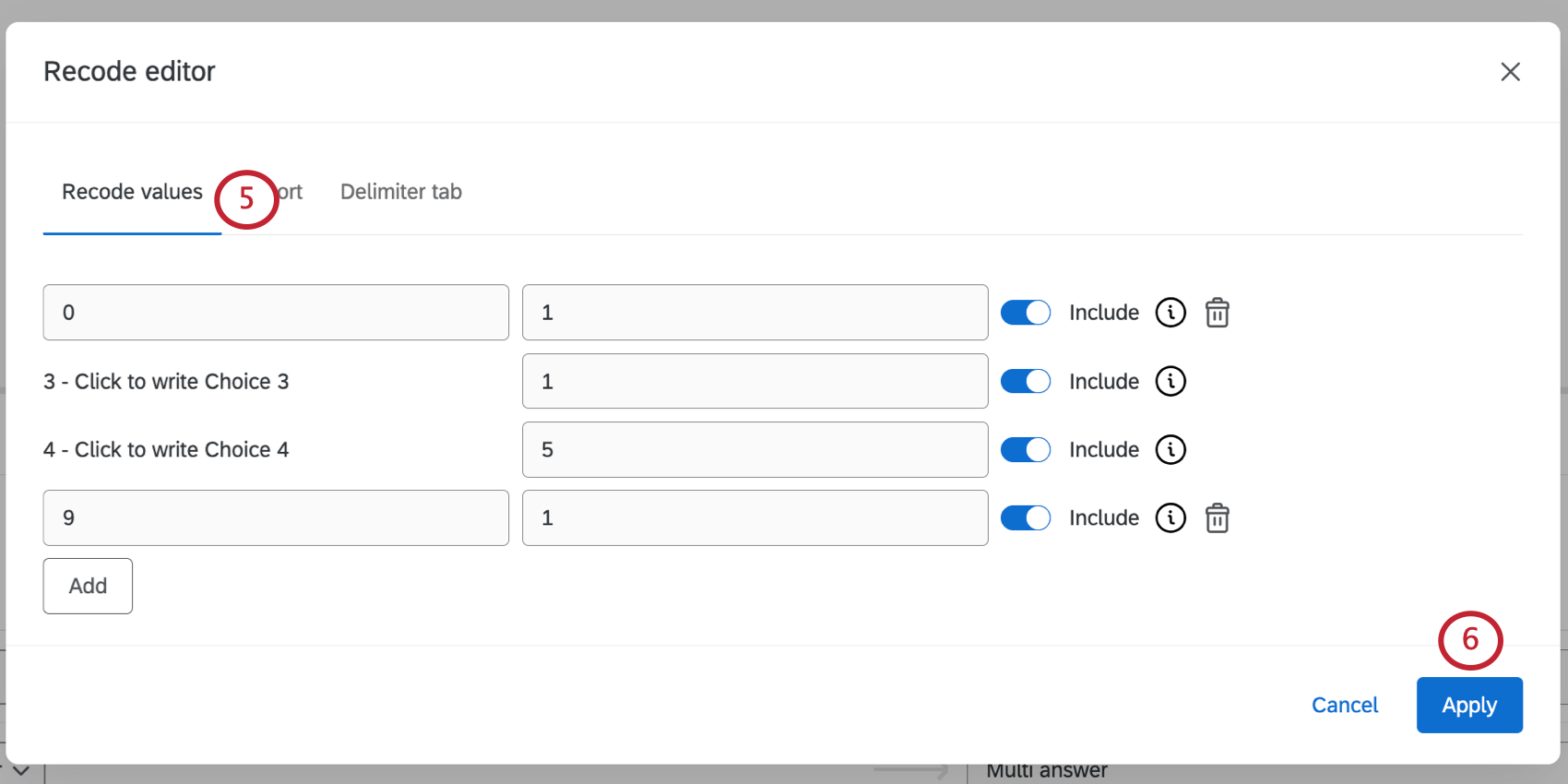
- Click Apply to save.
Common Uses for the Recode Editor
One of the most common use cases for recoding values is to group similar choice options together. The recode editor can also be used to clean up data values.
While the following links go to the data mapper support page on recode values, the same functionality can be applied in the data modeler.