Creating a Data Model (CX)
About Creating a Data Model
The data modeler can be used to create datasets where you flexibly combine data from multiple types of sources. The data modeler has nearly all of the features the data mapper does, but with some additional advanced functionality, such as left outer data joins. The data modeler also makes it easier than ever to map not just survey data, but data from your directory, tickets, and other data sources, while allowing you to combine them in the same dataset.
Incompatible Features
The following features aren’t compatible with data models yet:
- Page templates
- Date time segmentation
- Spotlight Insights
- Org hierarchies
- XM Respondent Funnel page templates (XM Respondent Funnel dataset is compatible)
- Distribution reporting
Creating a Dataset with the Data Modeler
- Create a new dataset.
- Under Type, select Data modeler (joins).
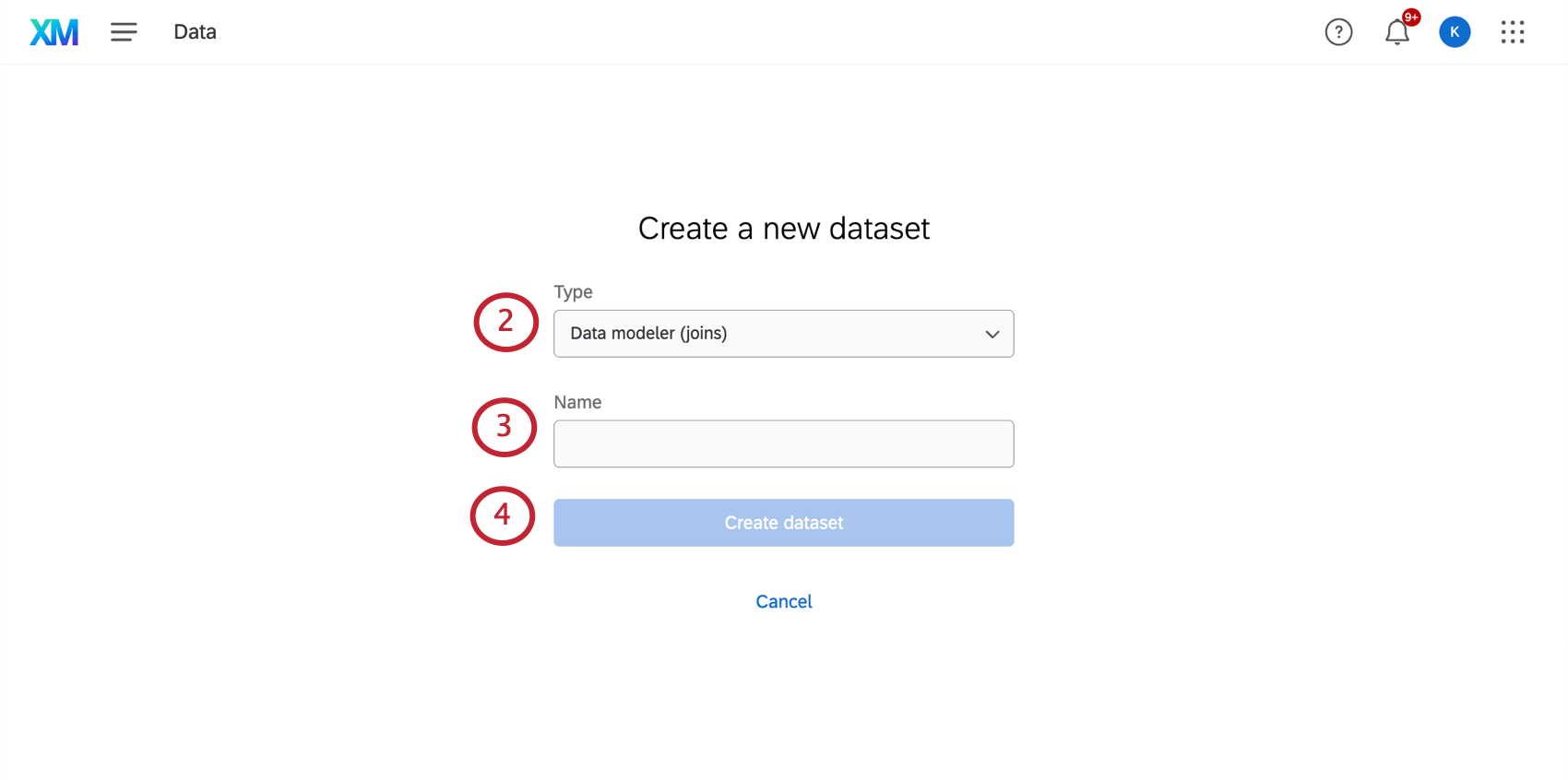
- Name your dataset.
- Click Create dataset.
- Click Add Source.
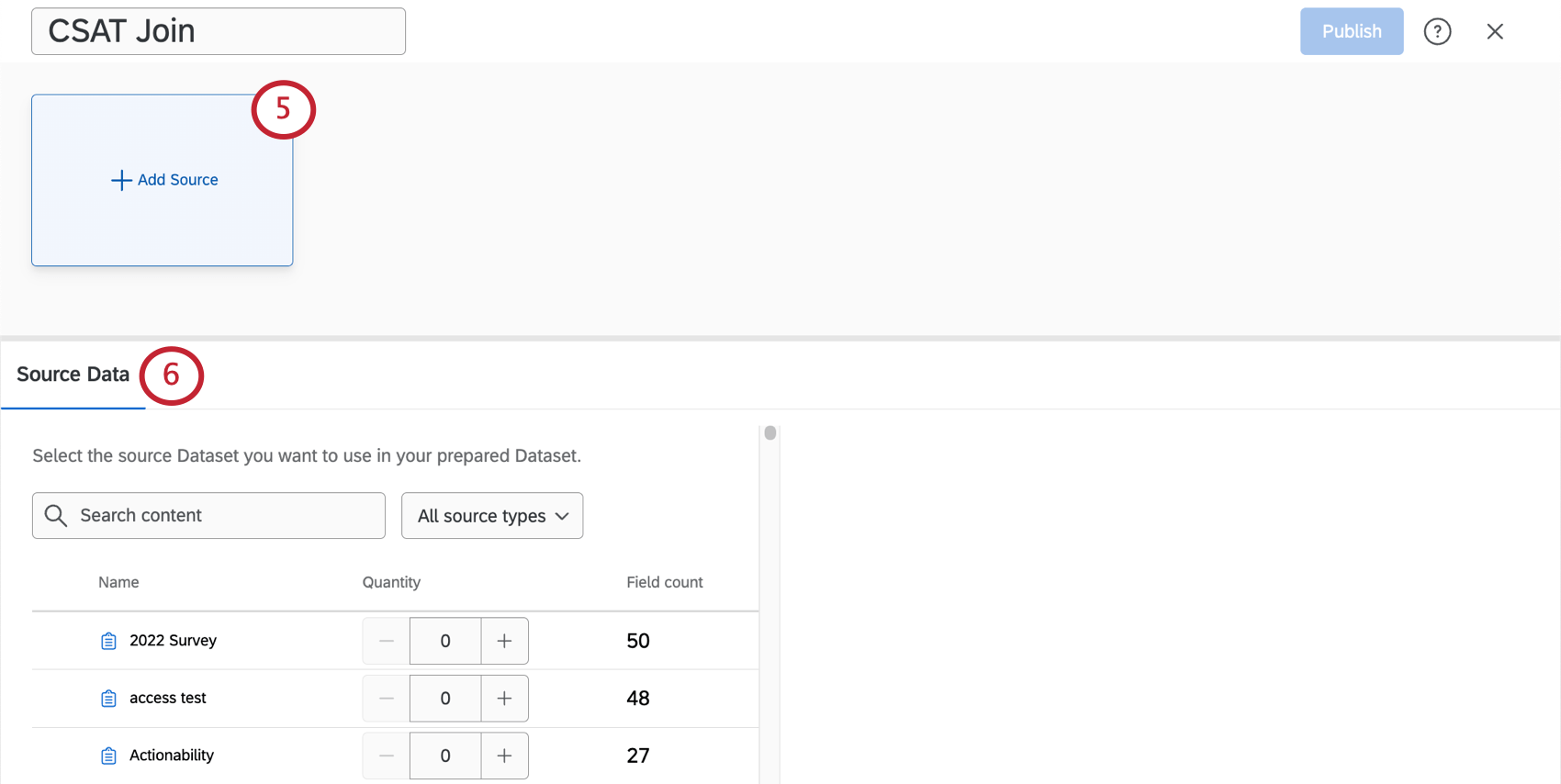
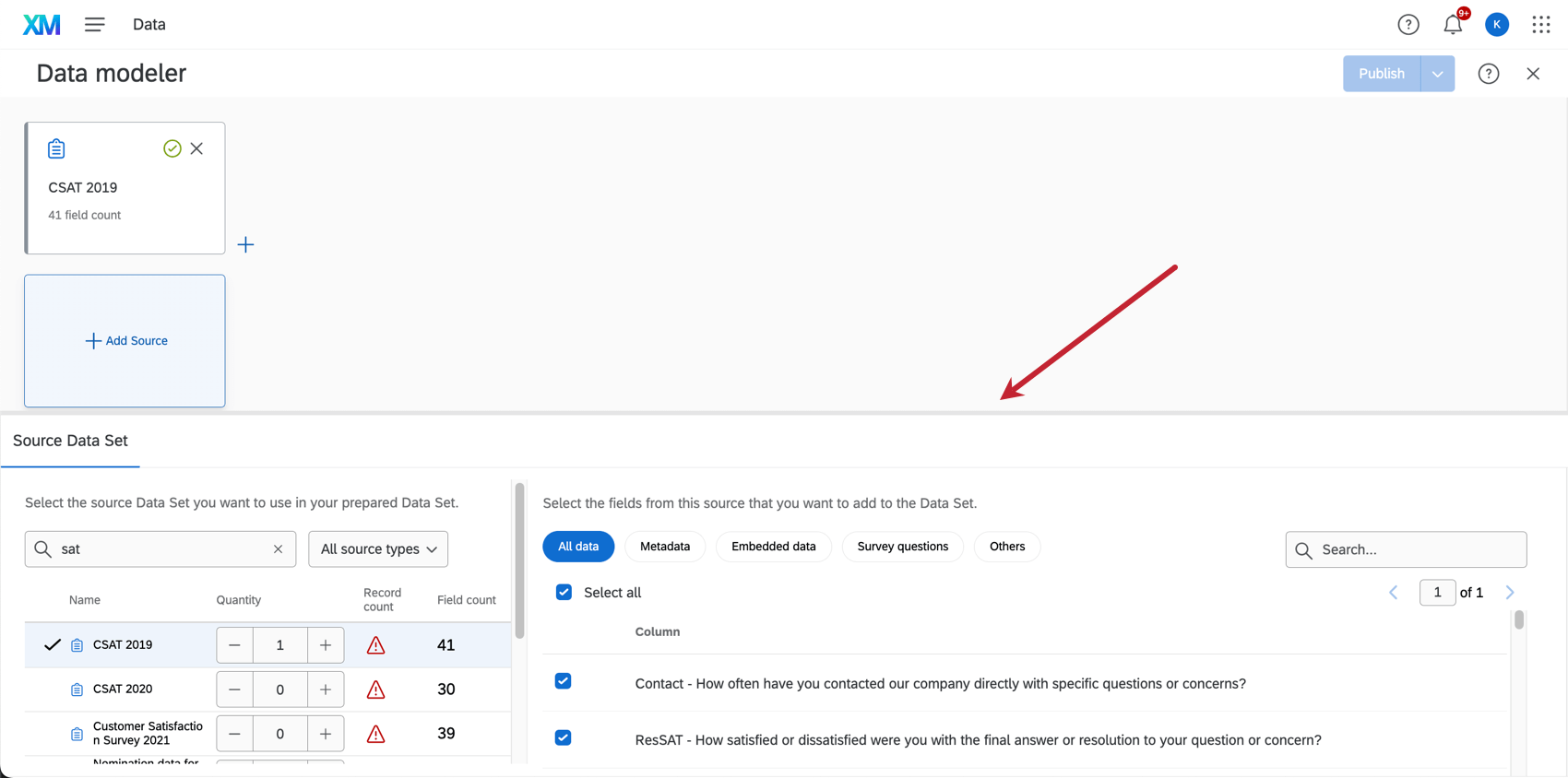
- Under Source Data, choose a survey, ticket set, directory, or another external data source. Use the search bar and All source types drop-down to find a source.
Qtip: Only tickets created from surveys can be mapped with the data modeler. You need to be either the owner of the associated survey or a collaborator with both Edit and View reports access.Attention: Only projects you have access to will appear in this list. If any projects aren’t showing up, make sure you have been invited to collaborate on them.Attention: Legacy distribution reporting is not compatible with the data modeler.
- When you’re ready to select a source, adjust the Quantity to 1 (or more, if desired).
 Qtip: It can be useful to add the same source more than once if you plan to perform separate unions and joins in your dataset. You cannot create a union or a join with multiple copies of the same source.
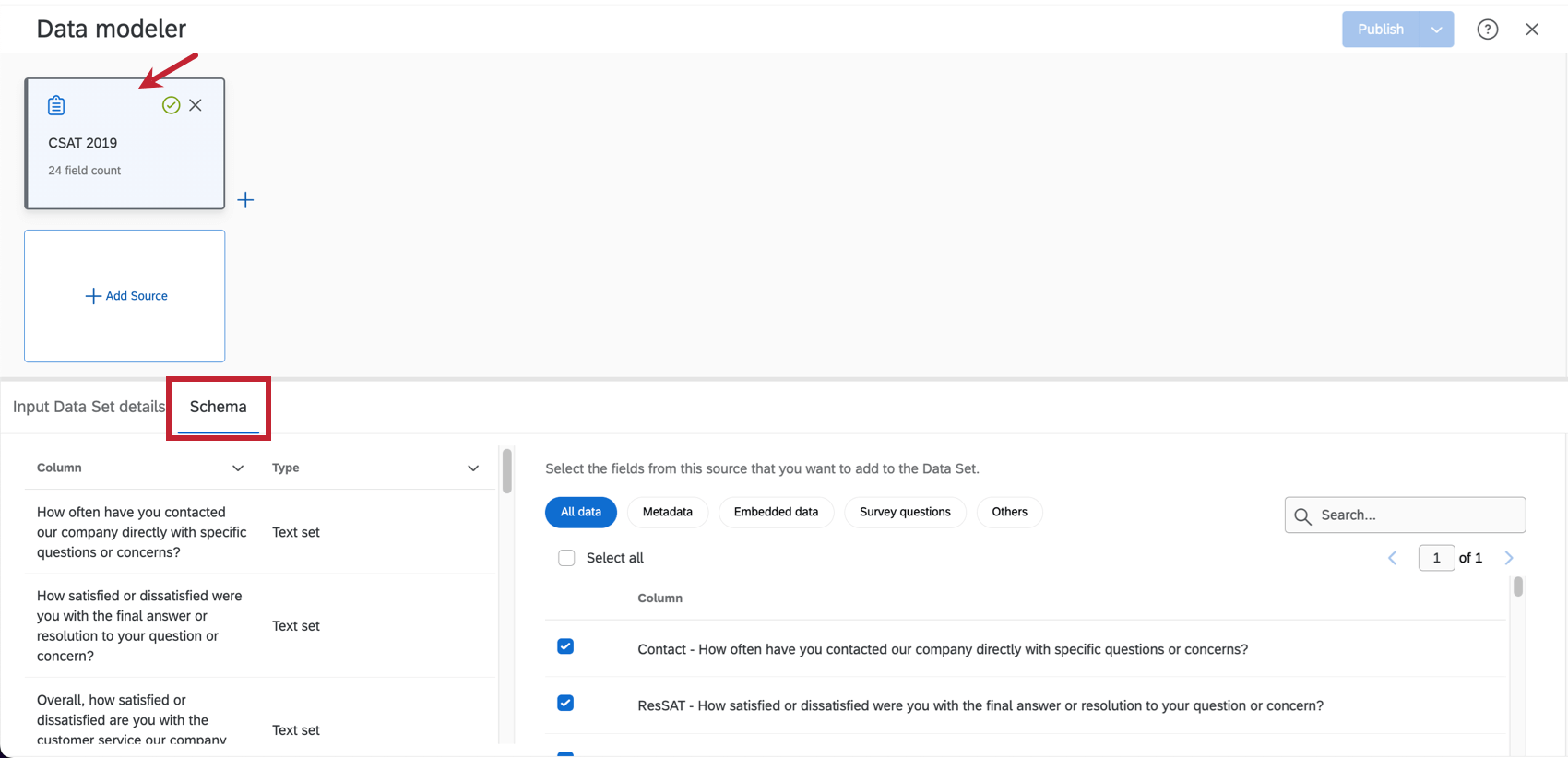
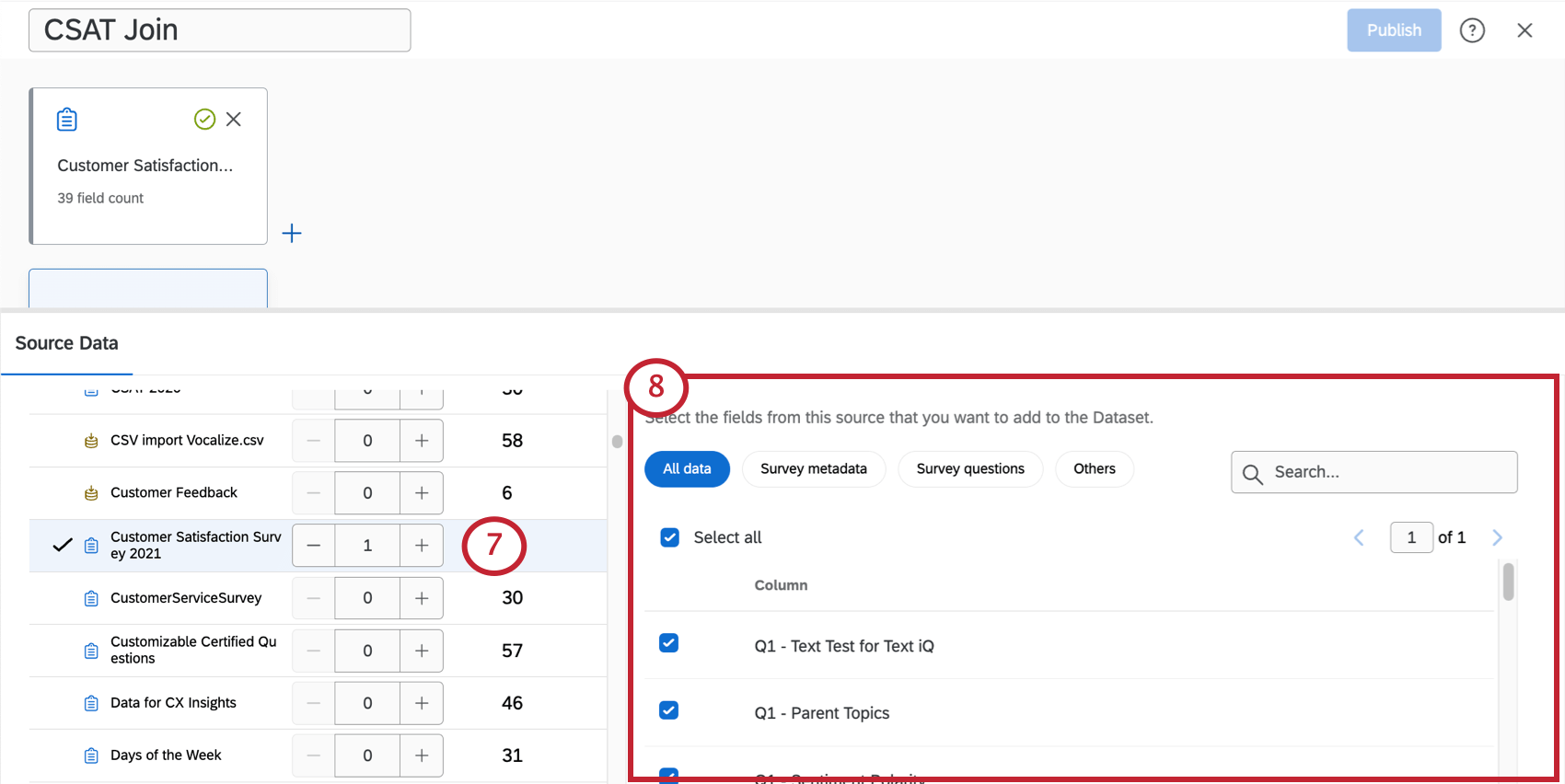
Qtip: It can be useful to add the same source more than once if you plan to perform separate unions and joins in your dataset. You cannot create a union or a join with multiple copies of the same source. - Select all the fields you want to include in your dataset. You can click on different types of data, like “Metadata”, to see only those fields, or use the search bar to search for specific fields.
Qtip: When selecting fields to include in your data model, think about which fields will be important when analyzing your data. Fields that are commonly included are survey questions, important metadata, and the field you plan on using to join your datasets.
- Add more data sources, or perform joins and unions. See linked pages for more details.
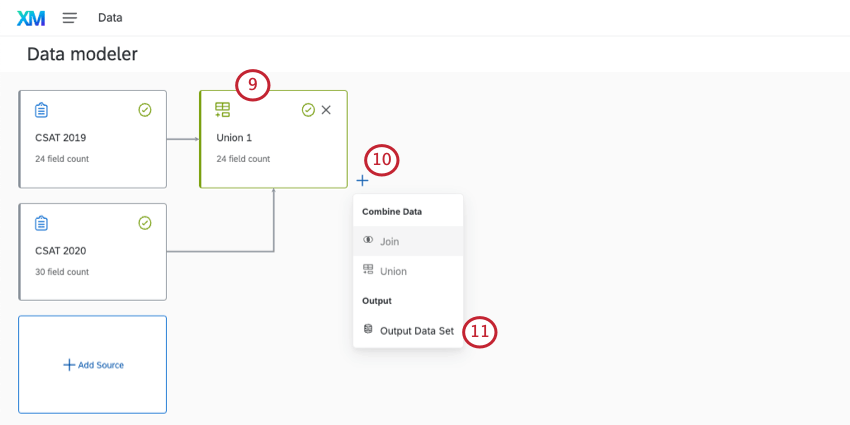 Qtip: If you want to report on 2 different surveys with 2 years worth of feedback data, you’ll most likely use a union. If you want to create a list of all of the customers who reached out across those years, you’d use a join.
Qtip: If you want to report on 2 different surveys with 2 years worth of feedback data, you’ll most likely use a union. If you want to create a list of all of the customers who reached out across those years, you’d use a join. - Once you’ve finished, click the plus sign ( + ).
- Select Output Data Set.
- Check the Dataset Editor for accuracy. Here, you can find all of your data fields.
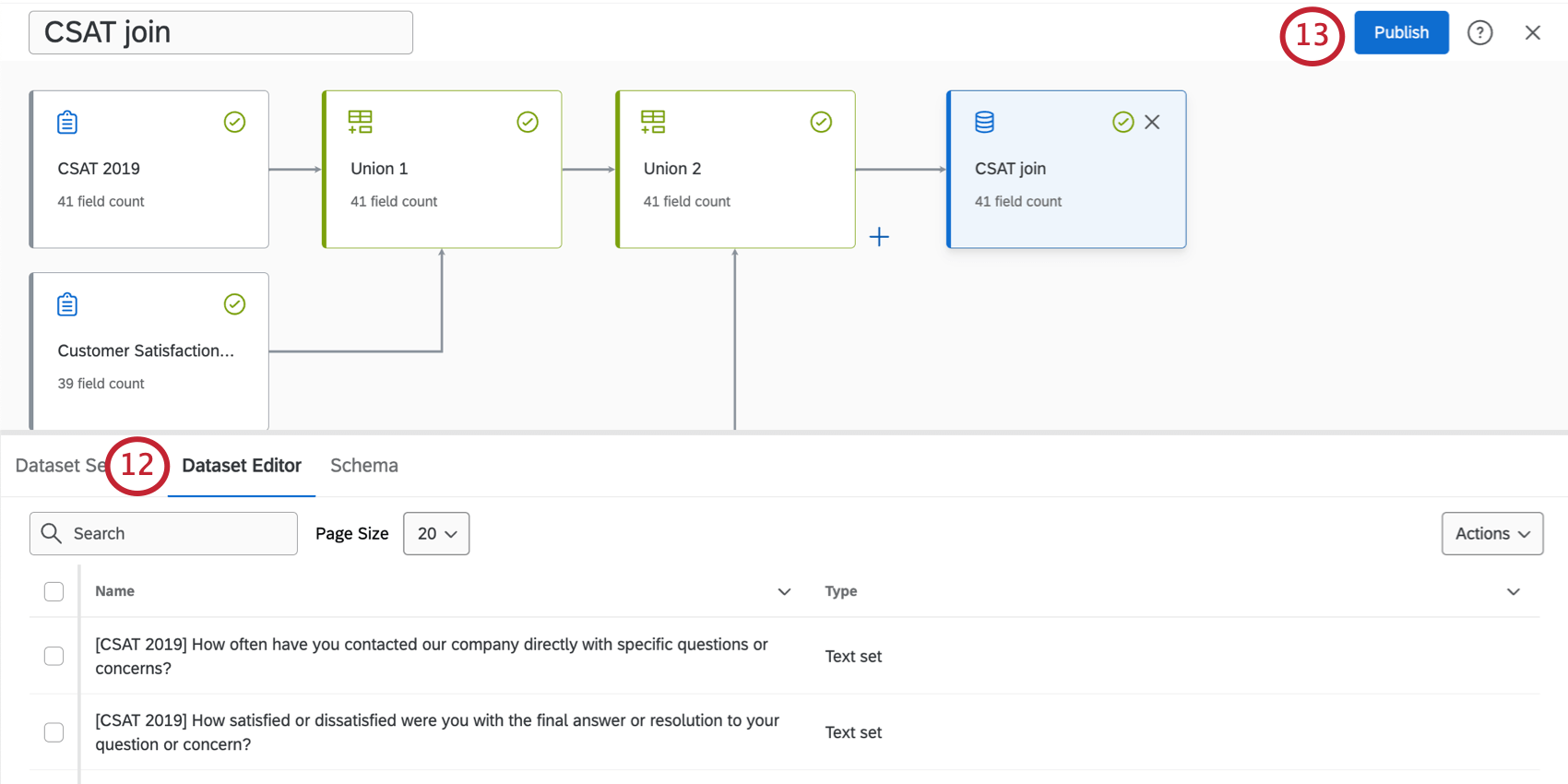 Qtip: If needed, you can always edit these fields later.
Qtip: If needed, you can always edit these fields later. - Select Publish.
Qtip: this will take you back to the Data page. See how to add your dataset to a dashboard.
Types of Sources Available in Data Models
A dataset gets its data from specific sources in Qualtrics. Data sources are often surveys, but there are many other sources you can add to data models.
- Survey project data.
- Tickets created from a survey.
Qtip: Only tickets created from surveys can be mapped with the data modeler. You need to be either the owner of the associated survey or a collaborator with Edit or View reports.
- Contact data from your directory.
Qtip: Directory data requires additional setup before it can be used in your data models. See Enabling the Contact Dataset.
- Assorted “External” sources, such as imported data projects, reputation management projects, and segment membership data.
Qtip: Segment data requires additional setup before it can be used in your data models. See Using Segment Data in Dashboards.
Continuous vs. Periodic Dataset Updates
For the most part, data model datasets update continuously. That means that as you collect more data in your sources, your dashboard receives that data accordingly, including all unions and joins and field remappings. Continuous updates ensure your dashboard’s data stays current.
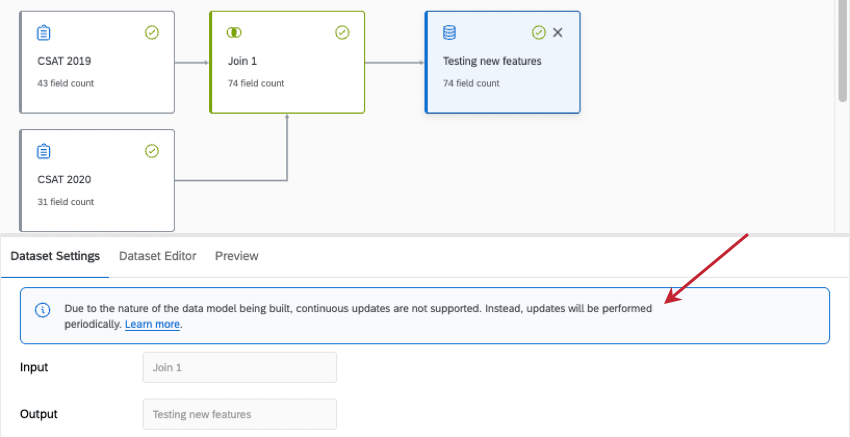
However, certain configurations in your data model can make it update periodically instead. Periodic updates exist to lighten the load on your dataset and ensure accuracy when particularly complex setups are involved. However, to get everything correct, the updates are slower.
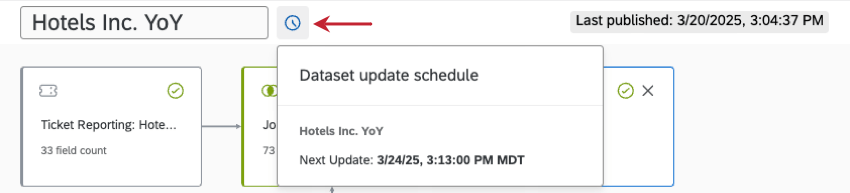
Periodic datasets generally update with new data weekly. Periodic datasets cannot receive new data before the weekly update, even after recaching. This schedule cannot be customized.
Qtip: To see the specific date and time a periodic data model will update, publish your changes. Hover over the clock that appears to see an estimate.
Identifying Features that Need Periodic Updates
Here are a few examples of features that cause a dataset to become periodic instead of continuous:
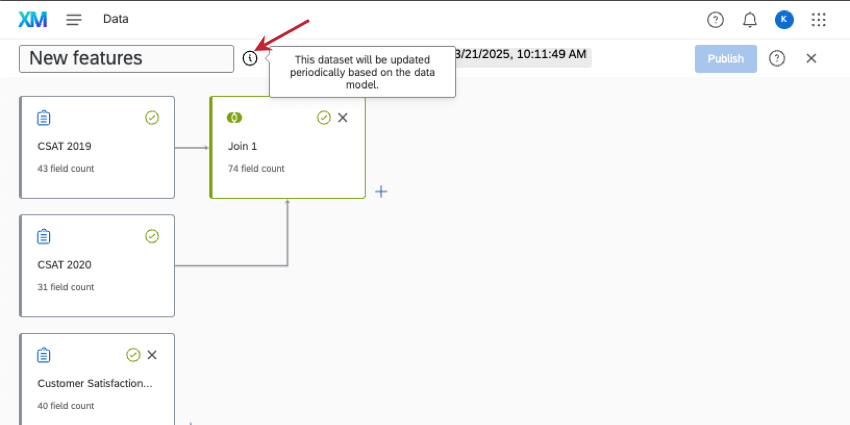
This list is not exhaustive. If your dataset updates periodically instead of continuously, there are a few places you can look in the data modeler to find this out:
Example: As soon as you finish a change that switches the dataset to periodic, this message appears in the information icon next to the title.
Dashboards You Can Add Data Models To
Data models can only be added to the following types of dashboards:
- Dashboards projects (also known as CX Dashboards)
- Dashboards added to programs
- Dashboards built into certain XM Solutions
- Brand Experience
See Dashboard Data for steps to add your completed data model to your dashboard.
This feature cannot be used with any Employee Experience dashboards or with Results Dashboards. For a similar Employee Experience feature, see Data Models.