Web Service Task
About the Web Service Task
The Web Service task is useful if you are experienced with API and would like to trigger different workflows within the Qualtrics software, or to an external web service, when the respondent finishes the survey. For example, if your survey collects the respondent’s contact information, then a web service task can use the create contact API call to add the respondent to a contact list.
We also recommend visiting these web service-related pages for more assistance and background:
- Qualtrics Developer Hub
- Web Service Methods
- API Documentation
- Passing Information via Query Strings
- Piped Text
Setting Up a Web Service Task
Depending on how you prefer to format your body parameters, the setup will slightly differ. If you are using JSON or XML format, enter your body in the Body section. If you’d prefer URL-Encoded, you can add parameters as a query string to the URL field.
- Create a workflow (or select an existing one) in your project or in the stand-alone Workflows page.
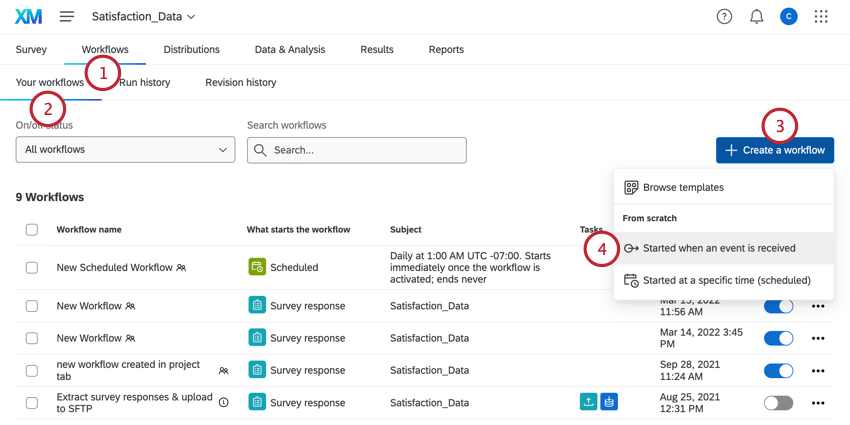
- Make sure you’re in the Your workflows section.
- Click Create a workflow.
- Determine the schedule or the event that triggers your task. (See a comparison.)
- Click Add task and select WebService.
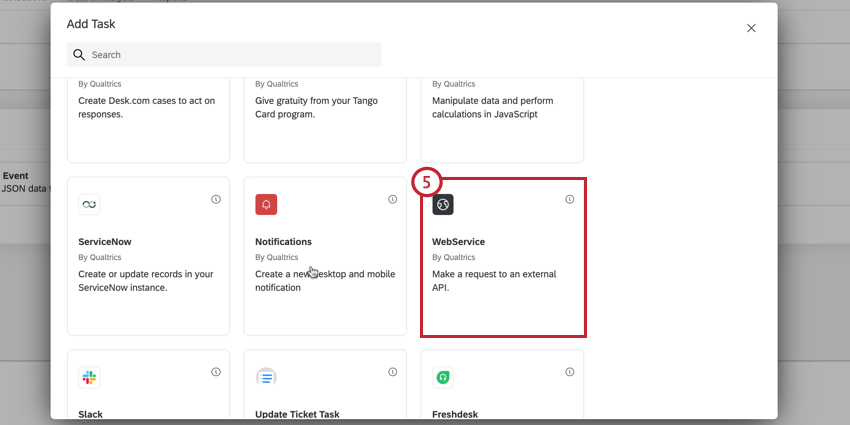
- Choose your authentication method. Your options include:
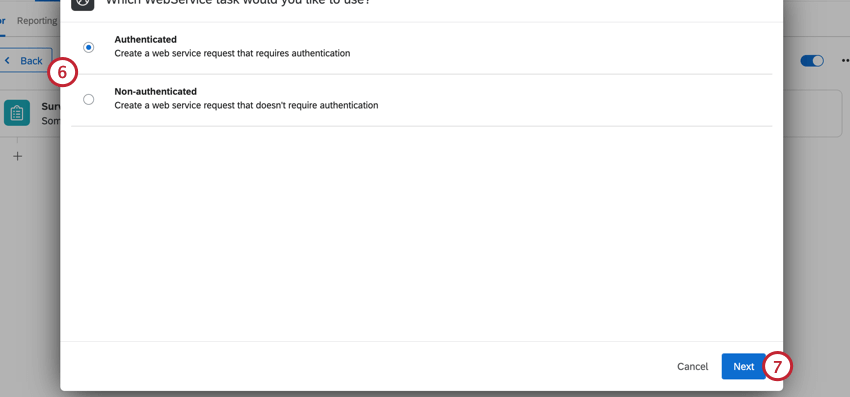
- Authenticated: Perform an authenticated web service request. Your authentication options include basic (with a password and username), API key, and OAuth.
- Non-authenticated: Perform a web service request without authentication.
- Click Next.
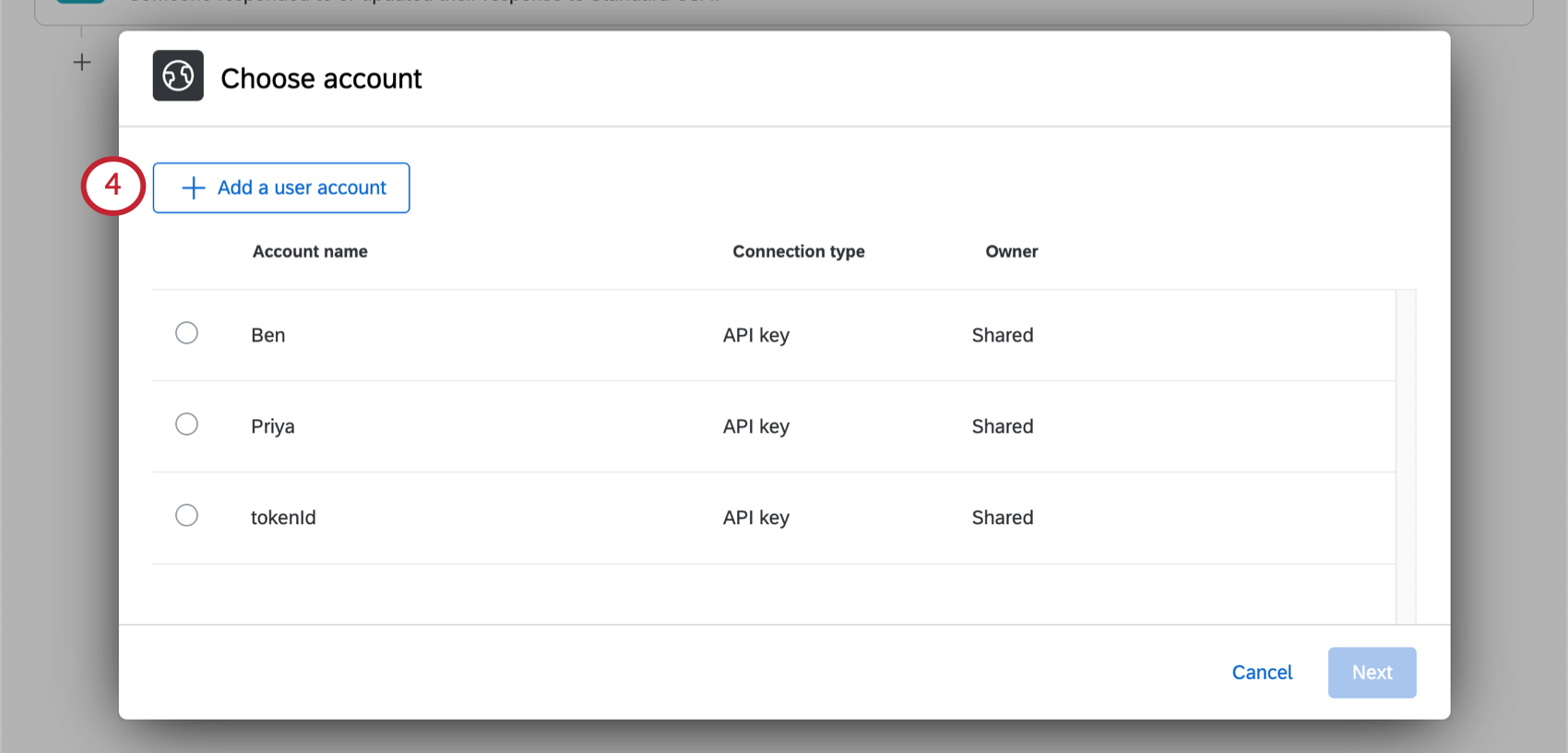
- If you selected an authenticated request, select your authorization credentials from the list, or click Add User Account to add new credentials. See Adding Authorization Credentials for more information.
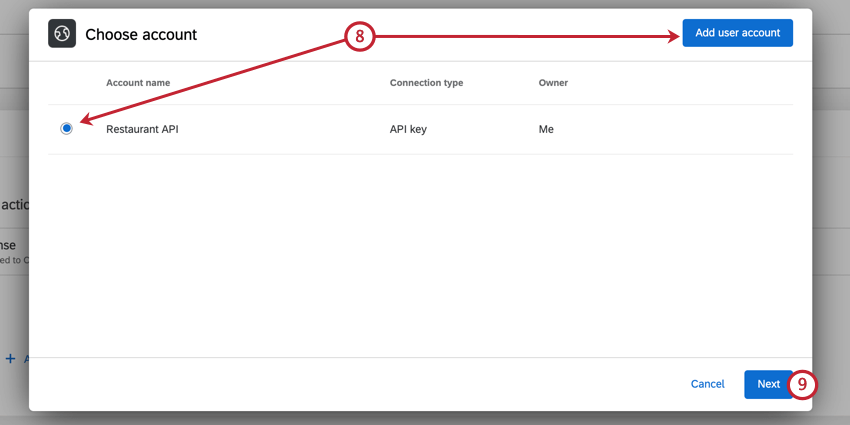 Qtip: You’ll be able to select any credentials you’ve previously added, or credentials added by a Brand Administrator in the Extensions tab.
Qtip: You’ll be able to select any credentials you’ve previously added, or credentials added by a Brand Administrator in the Extensions tab. - Click Next.
- If you’ve got a curl-formatted request, you can import it to automatically set your web service up. See the Using Curl Commands section for details.
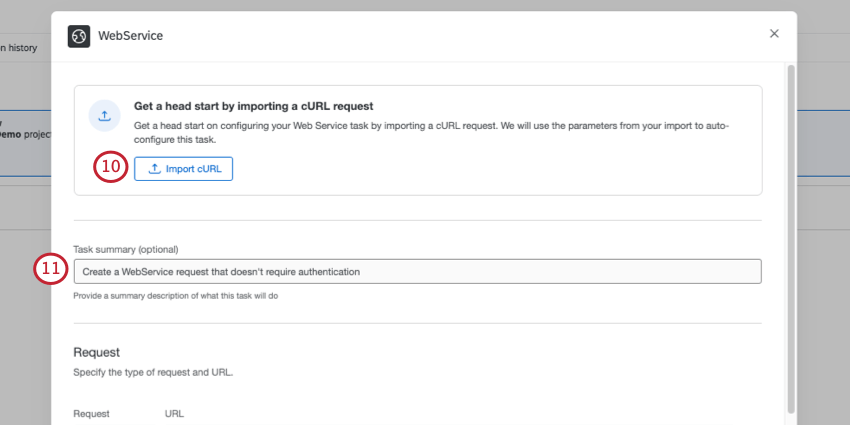
- If desired, add a Task summary at the top of your task. This is a description explaining the goal of the task.
- Choose your web service’s Request method. See Web Service Methods for more information about each method.
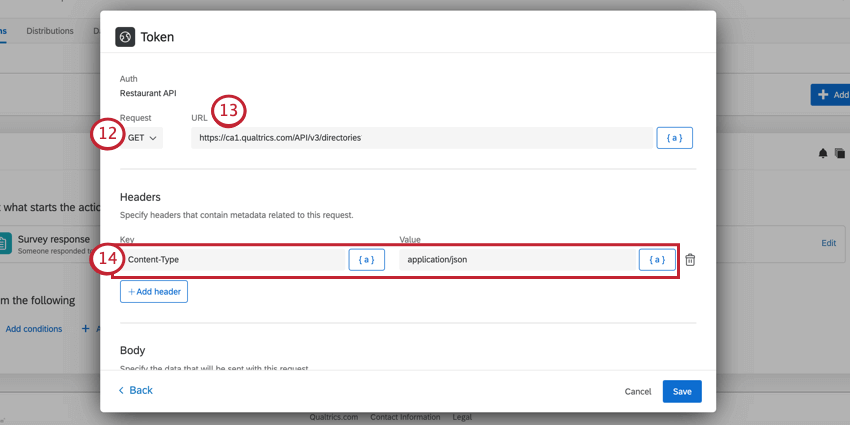 Qtip: If you’re using the Qualtrics API, the documentation will tell you what type of request to use.Attention: WebService tasks do not allow any URL redirects for non-GET requests. Only one redirect is allowed for GET requests.
Qtip: If you’re using the Qualtrics API, the documentation will tell you what type of request to use.Attention: WebService tasks do not allow any URL redirects for non-GET requests. Only one redirect is allowed for GET requests. - Enter the URL for your request.
Qtip: You can limit the domains that the web service task can connect to by specifying the domains in your extension domain settings.
- If desired, click Add header to add a header. Specify the Key and Value. To remove a header, click the trash can icon next to the header.
Qtip: Use the piped text icon, {a}, to insert piped text to pull in values from survey responses or previous tasks in the workflow.Attention: If using the Qualtrics API, you must include your API token through the header. See Adding a Header for Qualtrics API Requests for more information.
- If you chose post, put, or patch, you’ll need to choose the format of your body. Options include JSON, URL-Encoded, XML, and Plain Text.
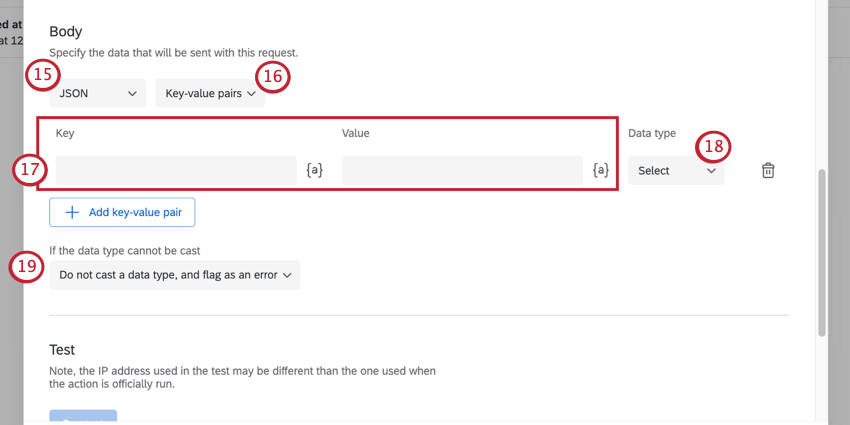
- Determine how you want to specify the body of your request. You can add the body as Key-value pairs or Free text.
Qtip: The maximum character count for both key-value pairs and free text is 75,000.
- If you selected Key-value pairs, add the Key and its associated Value. Click Add key-value pair to add additional parameters.
Attention: For POST, PUT, and PATCH requests you must specify a data type for each key-value pair.
- Select a Data type.
- Boolean: Select this data type if your data has one of two possible values.
- JSON: Select this data type if your data is in JSON format.
Qtip: Make sure that the inputed data is a valid JSON. When using piped text, ensure that special characters are not included.
- Number: Select this data type if your data is numeric.
- String: Select this data type if your data is in text format.
- System Default: Select this data type if you want to use the native data type for your data. If a data type cannot be found this will default to the String type.
Qtip: We recommend selecting one of the other data types to ensure your data is cast correctly.Attention: Key-value pairs that were configured before September 16, 2022 will have a data type of System Default.
Qtip: The Data type field is only available when you select JSON and Key-value pairs in steps 13-14. - Select what happens if the data type cannot be cast.
- Do not cast a data type, and flag as an error: If the data type cannot be cast, no data type will be cast and the task will fail. This can be seen in the Run History tab.
- Cast the data type to system default: If the data type cannot be cast, the data type will be set to System Default.
- If you selected Free Text, enter your body parameters in your selected format.
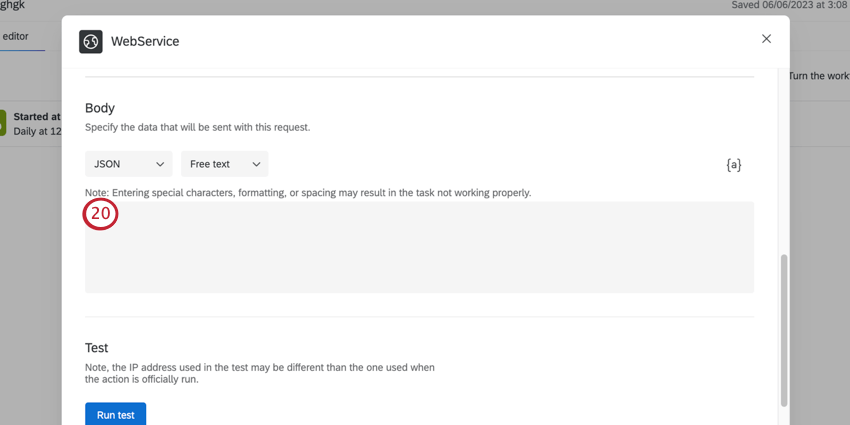 Attention: You should not leave this field empty or have keys without values. Instead, either don’t include the field at all, or enter the term “null” to indicate empty values. We recommend excluding the field.Qtip: If a web service task encounters an invalid JSON body, the task will not fail. Instead, the invalid JSON will be converted into a string and saved as a “text” property in a new JSON object. That way, you’ll be able to see the invalid text once the task finishes processing.Attention: Web service tasks do not currently support comments.
Attention: You should not leave this field empty or have keys without values. Instead, either don’t include the field at all, or enter the term “null” to indicate empty values. We recommend excluding the field.Qtip: If a web service task encounters an invalid JSON body, the task will not fail. Instead, the invalid JSON will be converted into a string and saved as a “text” property in a new JSON object. That way, you’ll be able to see the invalid text once the task finishes processing.Attention: Web service tasks do not currently support comments. - To test your web service, click Run test.
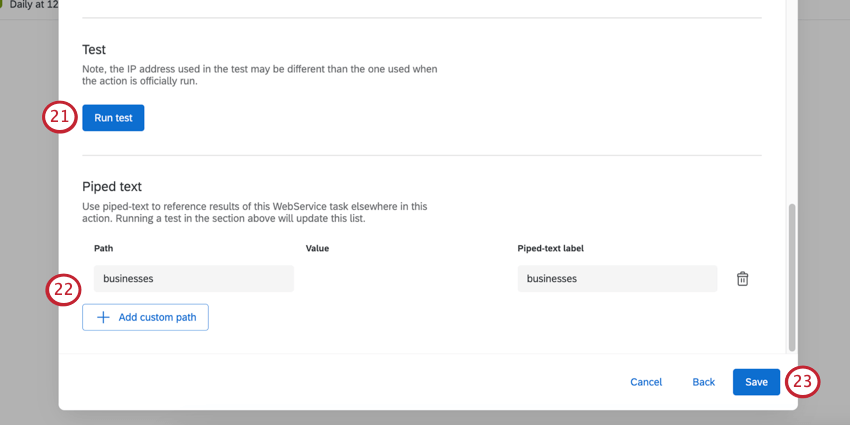 Qtip: After clicking Run test, the result of your request will appear, letting you know if it was successful or not, and the resulting JSON or XML, if it was successful.
Qtip: After clicking Run test, the result of your request will appear, letting you know if it was successful or not, and the resulting JSON or XML, if it was successful. - Click Add custom path to add JSON or XML paths. These paths let you use the results of your web service in piped text, to be used with other tasks in your workflow, such as a code task. If you tested your web service, you may automatically have values here, as Qualtrics will automatically pull them out of the results.
Qtip: Click Add custom path to add additional paths, or click the trash can next to a path to delete it.Attention: Data from a failed task cannot be piped into another task. The piped text will display as a null value.
- When finished setting up your workflow, click Save.
Using the AI Assistant for Task Set Up
The AI Assistant can configure the API integration in web service tasks by reading publicly available API documentation and setting up the task automatically.
- Create a workflow with a Web Service task.
- Choose your authentication method. For more information, see Setting Up a Web Service Task.
- Click Try AI Assistant.
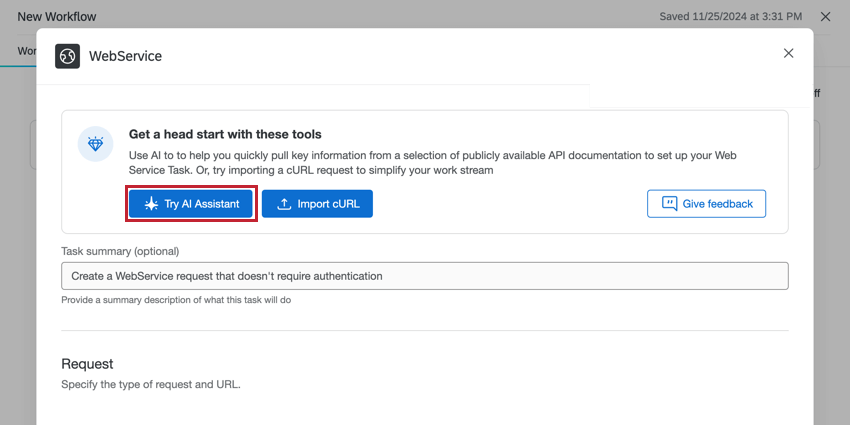
- Select the web service.
- Describe the intent or request of the API call.
- Click Generate draft.
Qtip: If the AI Assistant is unable to generate a draft, edit the request and try again.
- Review the API configuration.
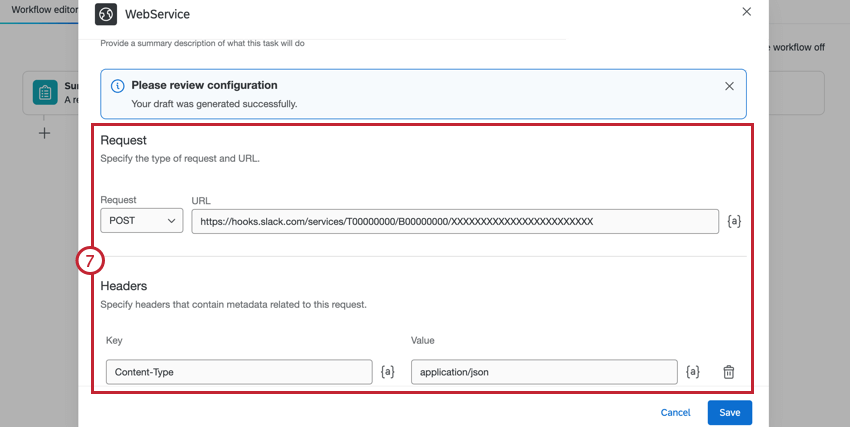
- To test your web service, click Run test.
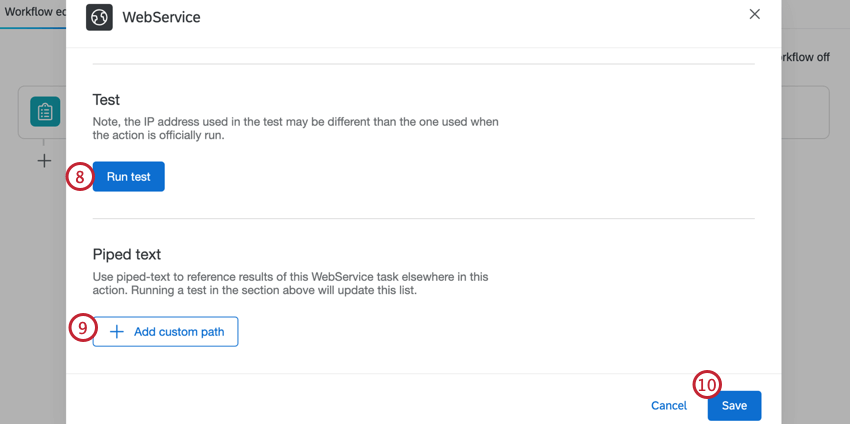
- Click Add custom path to add JSON or XML paths. For more information, see Setting Up a Web Service Task.
- Click Save.
Adding Authorization Credentials
This section covers how to add authorization credentials for the web service task. You can add credentials using the Basic, API Key, or OAuth 2.0 method. To add credentials, click Add user account from the credential selection window.
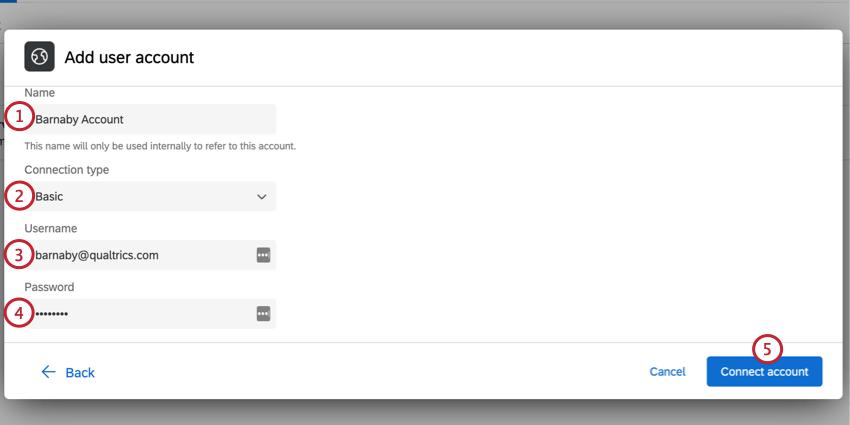
Basic
Basic authentication requires you login with your account’s username and password.
- Give your credentials a Name. This is for your organizational purposes only.
- Choose Basic as the connection type.
- Enter the Username required for authentication.
- Enter the Password for authentication.
- Click Connect account.
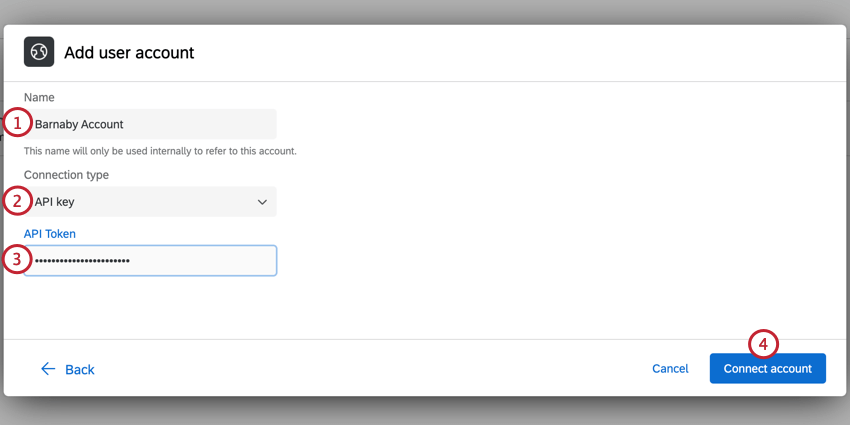
API Key
API Key authentication allows you to authenticate using a static API token.
- Give your account a Name. This is for your organizational purposes only.
- Choose API key as the connection type.
- Enter the API Token used for authentication.
- Click Connect account.
OAuth 2.0
OAuth2.0 authorization removes the need to use static API tokens or basic username and password to integrate with 3rd-party platforms. The web service task supports two different OAuth2.0 authorization types: authorization code and client credentials.
You can use OAuth 2.0 authorization to integrate seamlessly with many 3rd-party platforms. The Qualtrics web service implementation follows the official OAuth specification. However, some external systems may have slightly different configurations leading to incompatibilities with OAuth2.0 authorization in the web service task.
The following integrations are some examples that have been fully verified to work with OAuth2.0:
- Salesforce using the authorization code method.
- Jira using the authorization code method.
- Zoom using the authorization code method.
https://{dataCenter}.qualtrics.com/oauth-client-service/redirect, where {dataCenter} represents the value associated with your account. See this page for more details on finding your account’s datacenter.To authenticate using OAuth 2.0:
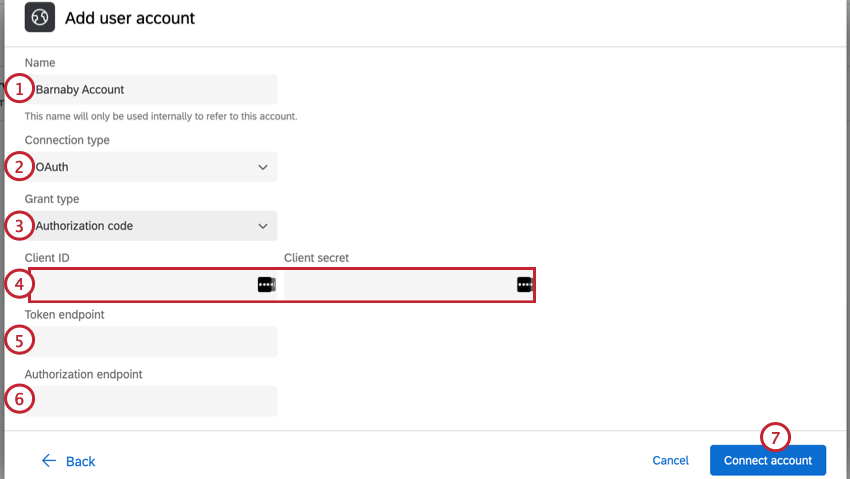
- Give your account a Name. This is for your own organizational purposes only.
- Choose OAuth as the connection type.
- Choose your Grant type, or how the access token is retrieved. You may choose:
- Authorization code
- Client credentials
- Enter the Client ID and Client secret.
- Enter the Token endpoint.
- If you selected authorization code as the grant type, enter the Authorization endpoint.
- Click Connect account.
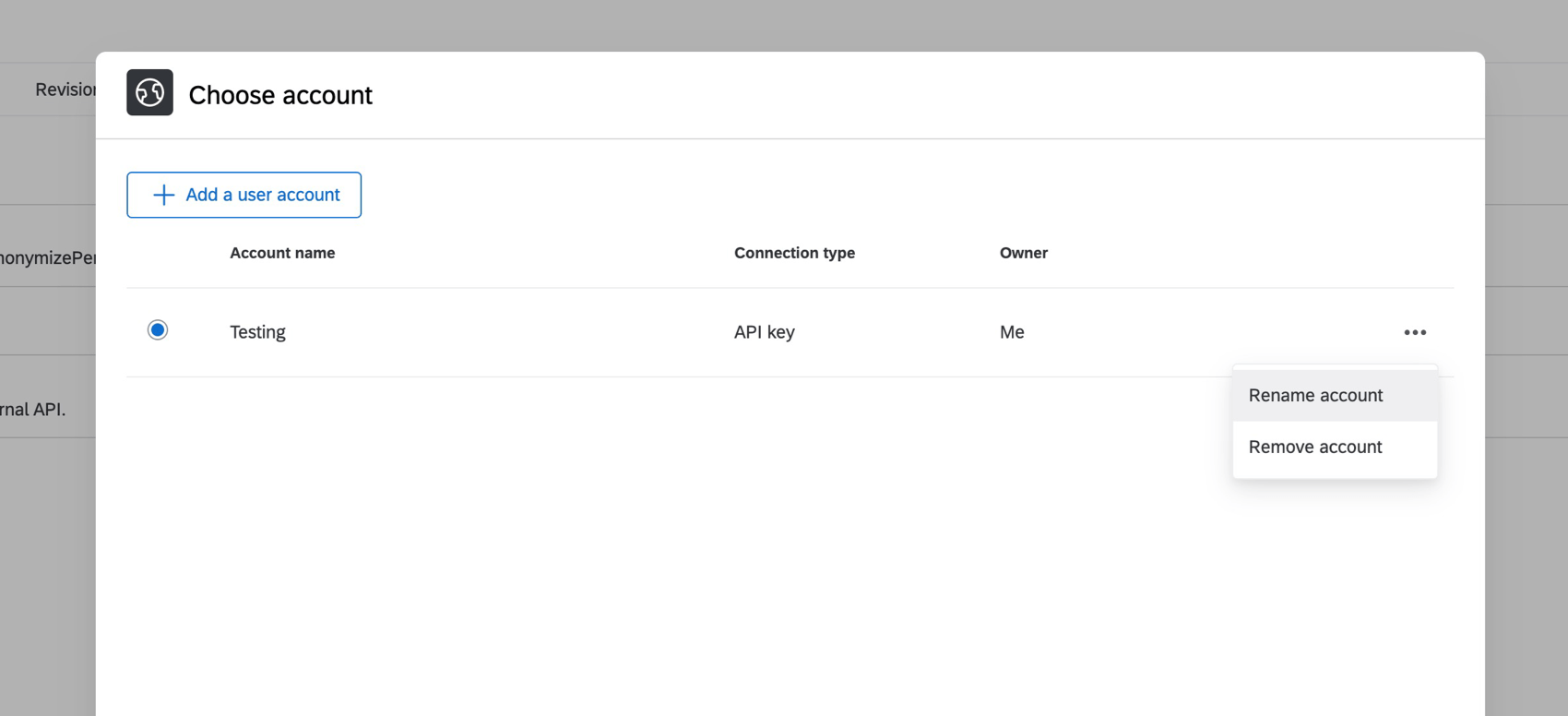
Renaming & Removing Credentials
To edit your credential’s name, click the three dots next to the account. To remove credentials, click Remove account.
Adding a Header for Qualtrics API Requests
When using the Qualtrics API, you must include your API token as a header in your web service.
- Set up your web service task, select your credentials, and choose your request.
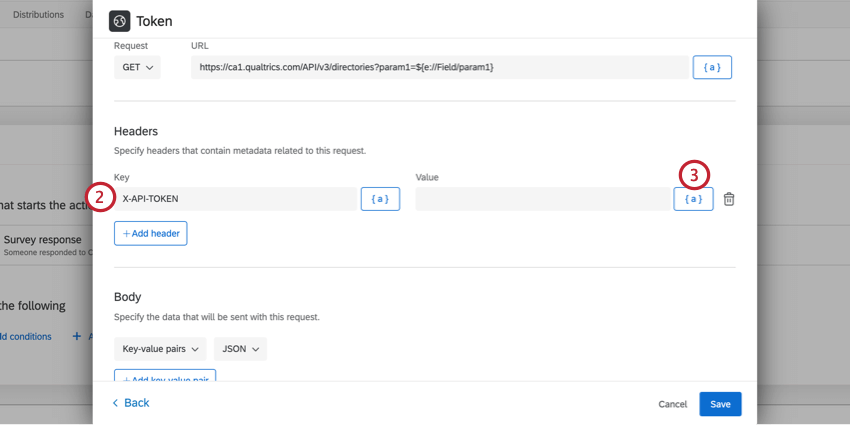
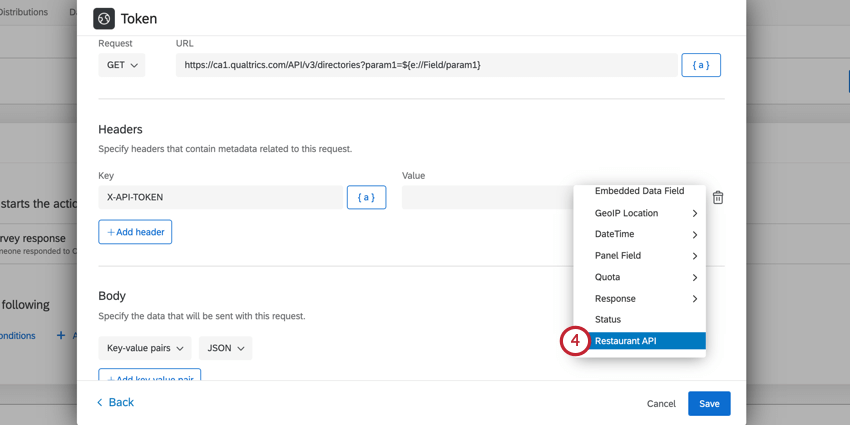
- In the Headers section, enter X-API-TOKEN as the Key.
- For the value, click the piped text icon, {a}.
- Select your credentials from the list.
Mutual TLS
Mutual transport layer security (mTLS) is an additional, optional layer of security on top of standard API authentication mechanisms (such as API Token or OAuth). Mutual TLS ensures both the person connecting to an API / web service and the API / web service itself have secure, encrypted traffic in both directions. Once mTLS is enabled, all requests must present the correct client certificate for requests to succeed. If a caller makes a request using an invalid or missing client certificate, the API they are trying to call will block the request.
Requirements
Every service varies in whether it supports mTLS and what format(s) it provides key information in. We are only guaranteed to support mTLS for services whose match our requirements:
- Provide a private key
- Private key can be formatted into PKCS8
- Provide a certificate
- Certificate can be formatted into X.509
The Qualtrics public APIs support mTLS as described above.
mTLS is only supported for Authenticated web services created in workflows. All three authentication methods are supported (Basic, API key, and OAuth2.0).
Adding mTLS
- Create your web service task.
- Choose Authenticated.
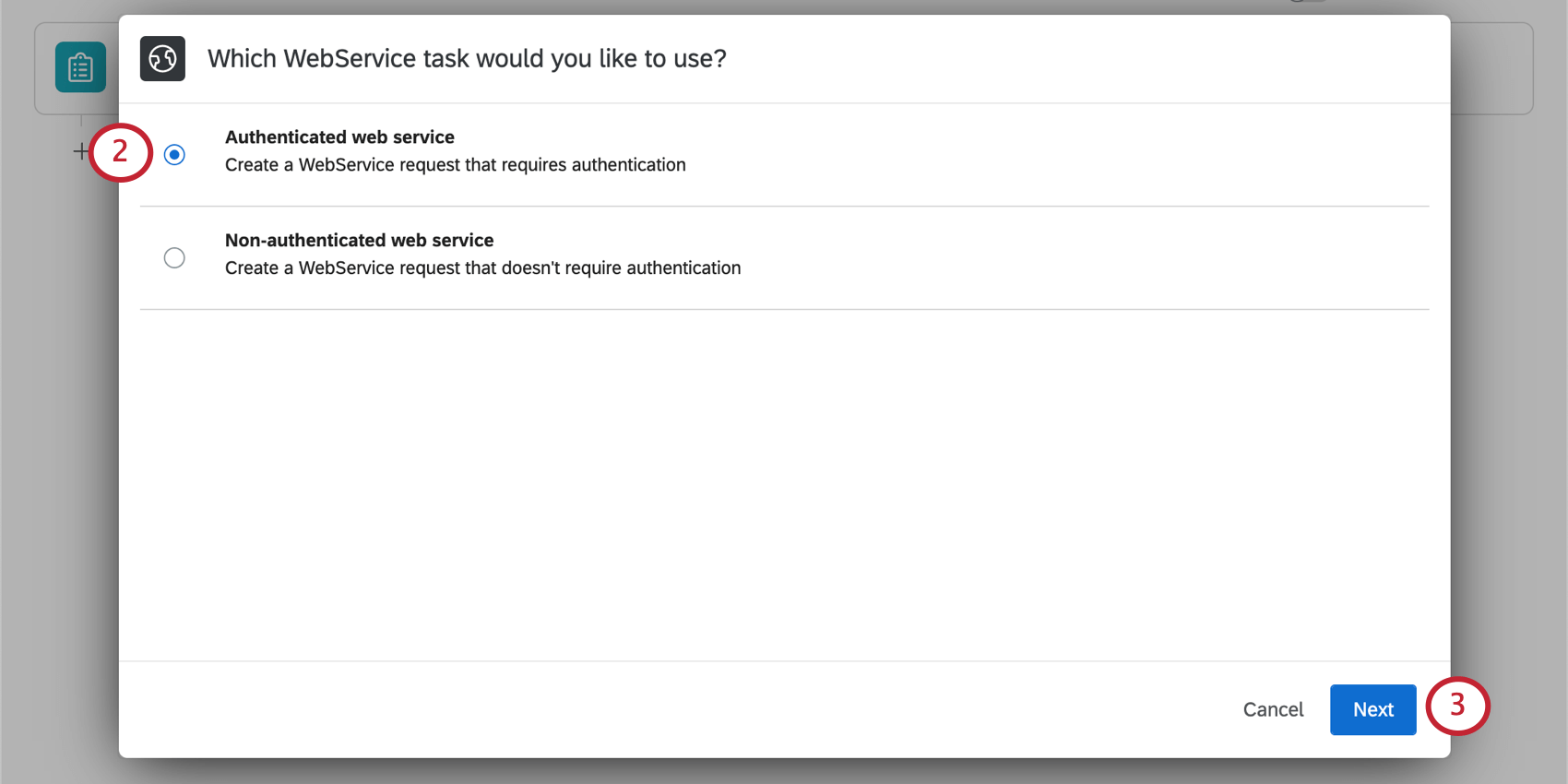
- Click Next.
- Add a user account.
- Select a connection type and fill out your credentials.
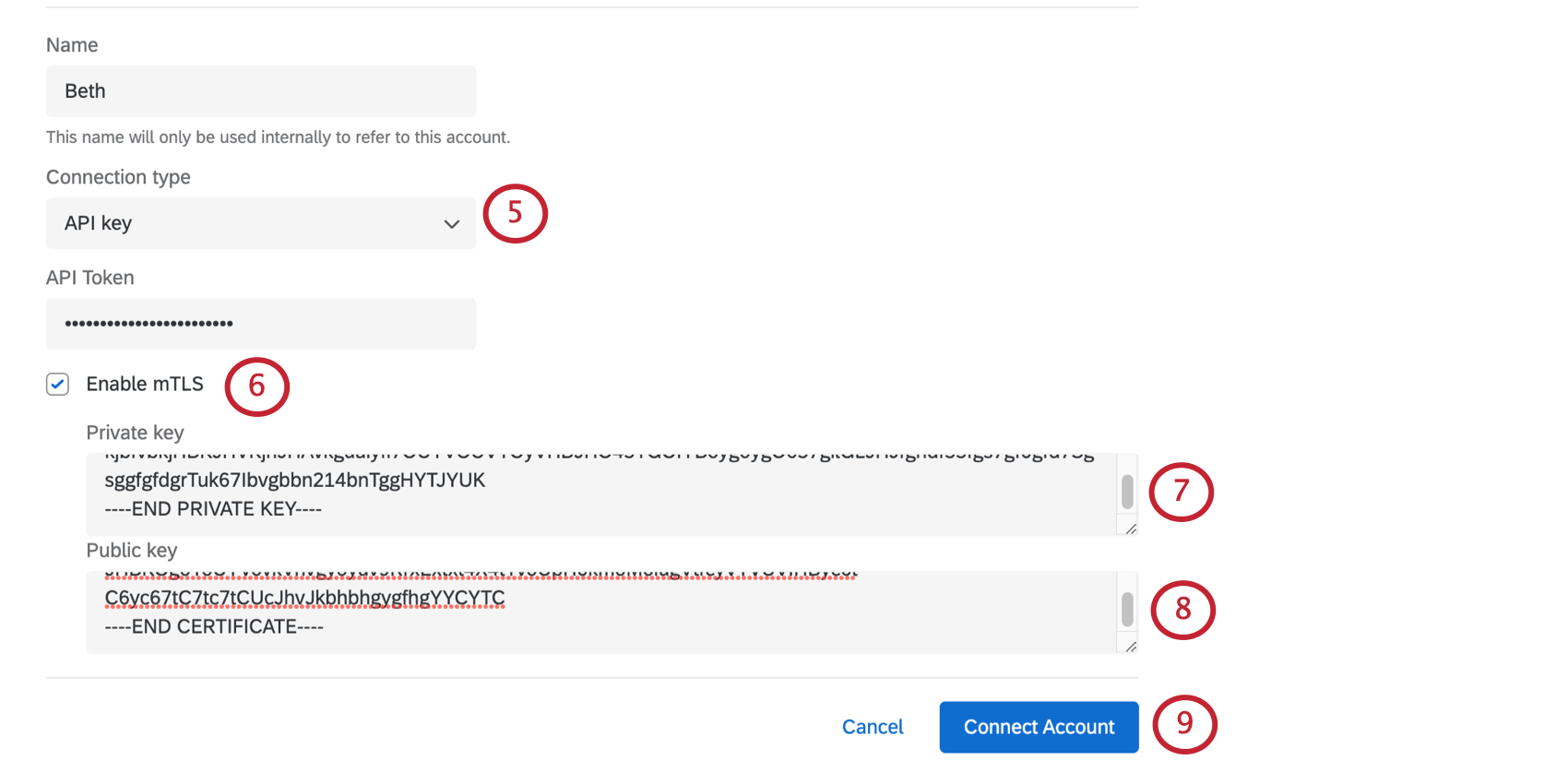
- Select Enable mTLS.
- The Private key can be thought of as the unique identifier of the client trying to connect. This value needs to be in PKCS8 format.
Qtip: If your key is in a different format, you can change use another program to change this format.Qtip: If you’re planning to use the Qualtrics API with your web service, see our API Documentation on mTLS. This documentation will show you how to pull the private key. When you paste the value in Qualtrics, you will need to include dashes that say “begin private key” and “end private key.”
- The Public key is the mTLS certificate. This value needs to be in X.509 format.
Qtip: If you’re planning to use the Qualtrics API with your web service, see our API Documentation on mTLS. This documentation will show you how to pull the certificate. When you paste the value in Qualtrics, you will need to include dashes that say “begin certificate” and “end certificate.”
- When you’re finished, click Connect Account.
- Proceed with your web service’s setup.
Using Curl Commands
Curl commands are one of many ways you can make HTTP requests, and are a valuable tool in passing information back and forth through URLs. You can import a curl command while you’re setting up your task to auto-populate different web service configurations.
Many API docs often provide curl examples you can use. Being able to copy and import these commands can thus make web service setup much quicker and easier.
For some examples of curl requests, look at the right on each of these API docs:
For a GET request, the curl command can be as simple as curl https://api.example.com/parameters. For curl commands that aren’t as simple as this, we’ll provide some common parameters.
Supported Curl Command Parameters
Here are some of the curl parameters the Qualtrics web service task supports:
| Parameter | Description | Curl command | Example |
| URL | The endpoint or resource the web service should interact with. | Full URL. | https://datacenter.qualtrics.com/API/v3/directories/ |
| HTTP Method | Options like GET, POST, PUT, and so on. | --X <command> or --request <command> | Example 1: --X GET Example 2: --request PUT |
| Headers | Custom headers. | --H or --header | Example 1: --header 'Accept: application/json' Example 2: --header 'Content-Type: application/json' |
| Body | The body (or payload) for POST requests. | --d or --data | --data '{
“description”: “Lists all open bugs”, “jql”: “type = Bug and resolution is empty”, “name”: “All Open Bugs” }’ |
| JSON format | Replace having to specify JSON formatting in the header and data. | --json | This curl command replaces the following 3 tags:
--data [arg] --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Accept: application/json" |
Common Header Parameters
Above, we mentioned you can use curl commands to define headers. Headers serve various purposes in HTTP communication, such as providing information about the request and controlling authentication. The specific headers you use depend on the requirements of the application or API you’re using.
Here are some examples of header parameters:
| Name | Description | Example |
| Accept | Specify the media formats for the response. | Accept: application/json |
| Content-type | In a request, content type specifies the media type of the resource sent to the server. In the response, the content type indicates the media type of the resource enclosed in the message body. | Content-Type: application/json |
| Authorization | Provide credentials for accessing a protected resource. | Authorization: Bearer token |
| ETag | Provide a unique identifier for a specific version of a resource. | ETag: "123456" |
| Content-length | Set the size of the entity-body in the message. | Content-Length: 1024 |
| Origin | Indicate the origin of the request. This can help with Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). | Origin: https://example.com |
Unsupported Parameters
Any curl parameters not listed above are not supported. Here are a few examples of curl command formats Qualtrics web service tasks do not support:
- --cookie to send cookies with the request.
- --L or --location for following redirects.
- --max-time for setting maximum request time.
- --o or --output for saving response to a file.
- --insecure to allow insecure connections.
- --A or --user-agent to specify user agent.
Importing Curl Commands
- During your web service task setup, click Import cURL.
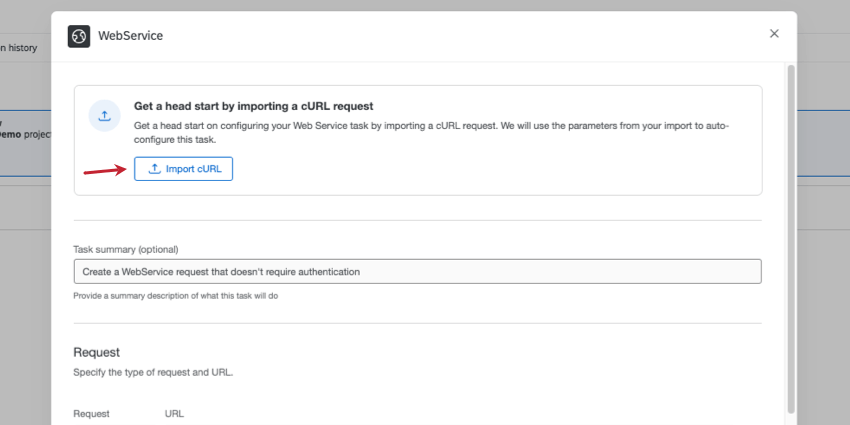
- Paste your curl command in the box.
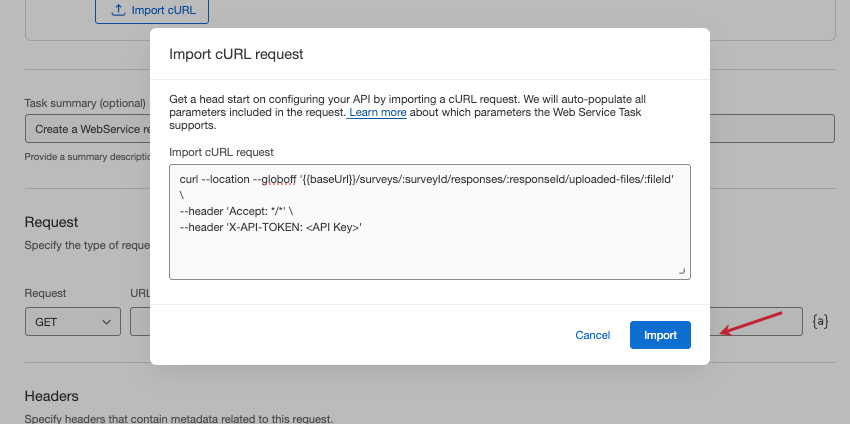 Attention: Make sure you include your HTTP method in your curl request, especially if you’re copying a curl command from another platform.Qtip: Keep an eye out for parts of the request you need to fill out with your own information. For example, in the screenshot above, you’d replace “API Key” with your API token.
Attention: Make sure you include your HTTP method in your curl request, especially if you’re copying a curl command from another platform.Qtip: Keep an eye out for parts of the request you need to fill out with your own information. For example, in the screenshot above, you’d replace “API Key” with your API token.Qtip: You can add a command in one single string, or you can mark line breaks using the escape character ( \ ). We do not support other line escapes (for example, ^ ). Here’s an example of a curl command with supported escape characters:
curl https://www.google.com/accounts/test \ -d accountType=GOOGLE \ -d source=Google-cURL-Example \ -d service=lh2 - Click Import.
- Web service fields will be filled automatically.