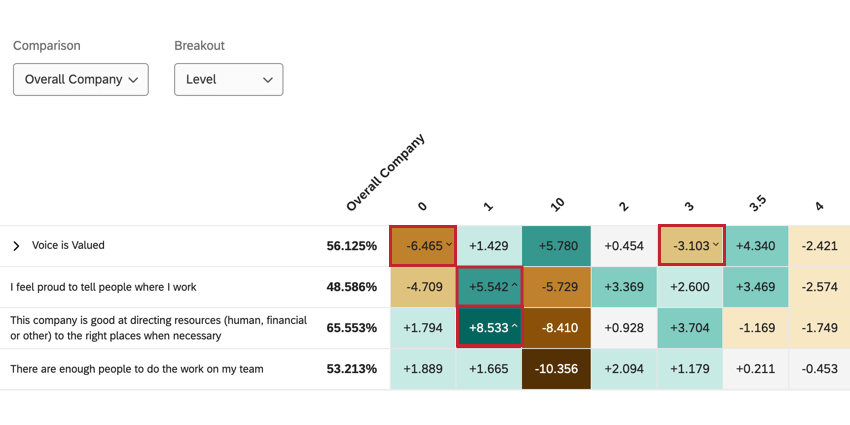
Heat Map Widget (EX)
About Heat Map Widgets
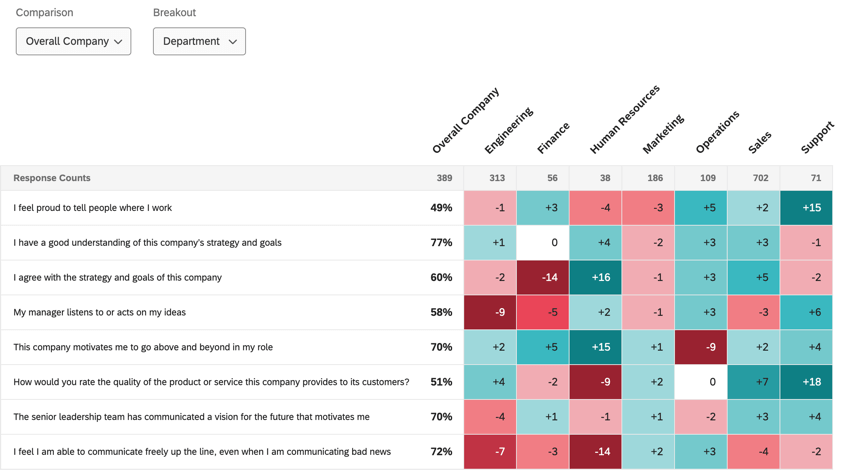
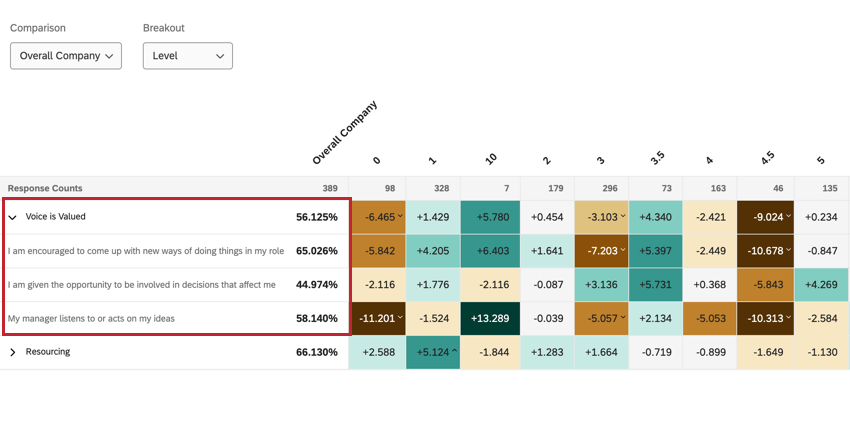
Heat map widgets provide an efficient way to quickly identify high points and low points across your organization or various demographic groups. These widgets are ideal for visualizing comparisons, showing how the many levels of a field compare on items across the organization. Heat map widgets are mobile accessible, and will resize and reformat as needed in a mobile browser.
Basic Set Up
This section covers how to set up a heat map widget.
- Add at least 1 comparison to your dashboard. You must have at least 1 comparison to use the heat map widget.
Attention: Create your comparisons in the order you’d like them to appear in the widget since the order is inherited from the Comparisons page.
- Add the heat map widget to your dashboard.
- Under Items, select the categories and survey questions you want to display. These items will be listed along the left of the widget. The order of these items is determined by the order the fields are mapped in your dashboard data.
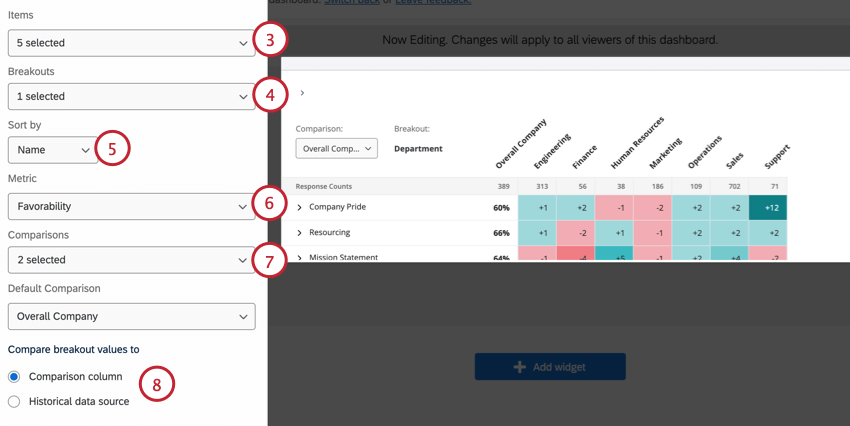
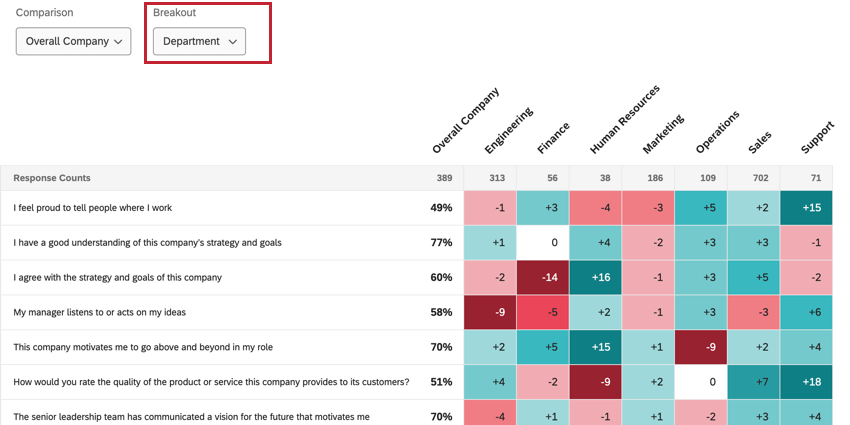
- Under Breakout, choose the field that you want to break your data out by. Usually this is a metadata field or org hierarchy, but you can also choose to break out by a survey question. You can choose multiple fields. Fields will be listed in the order they appear in within the dashboard data tab. Long field names may be shortened within the widget.
Qtip: It’s best to choose demographics, teams, and other tangible groups, such as Departments, Regions, and Tenure. Fields like Employee ID have too many values, and are too specific to the employee for the data to help you create company-wide action items.Qtip: The one-level-below breakout will not work with any hierarchy unit that has more than 100 sub units.Attention: If you have a breakout for a field marked as identifiable, and if a value for that breakout has a number of responses that falls below the anonymity threshold for all items, then the breakout column will be removed from the widget and the data will not be displayed.
- Use the Sort by dropdown to choose how you want fields to be sorted in your widget. Your options include:
- Name: Fields are sorted alphabetically.
- Response Counts: Fields are sorted by the number of responses.
- Choose the Metric to display in your widget:
- Favorability: Base your data on favorability. This is calculated as an engagement score, the percentage of participants who rated favorably on the set scale. For more on setting favorability scales, see scales.
- Average: Base your data on the average value. In a heat map, that means you see the average of everyone’s score in a group.
Qtip: Depending on the number of scale points, it may be difficult to get a large range for average. Consider adjusting your value ranges to include decimals.
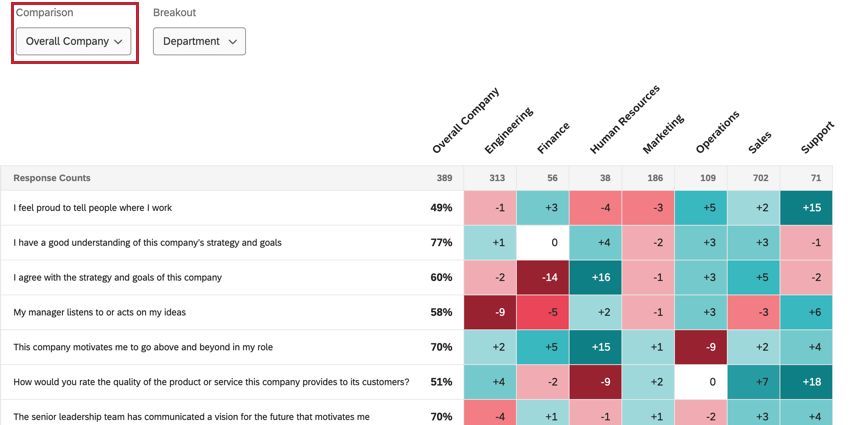
- Under Comparisons, choose at least 1 comparison to display in the widget. You can choose multiple comparisons.
- Choose what you want to compare your breakout values to:
- Comparison column: Values will be calculated by comparing the breakout’s score to the chosen comparison.
- Historical data source: Values will be calculated by comparing the breakout’s score to a historical data source that is mapped to your dashboard. If you select this option, a second menu will appear for you to choose the historical data source. For more on how to correctly set this version up, see Historical Data Comparisons.
Data Display Options
This section covers the options available to you for displaying your data in the heat map widget.
Enable Statistical Significance
The Enable statistical significance option allows you to flag if the differences displayed in your heat map widget are statistically significant. See Significance Testing for more information on this option.
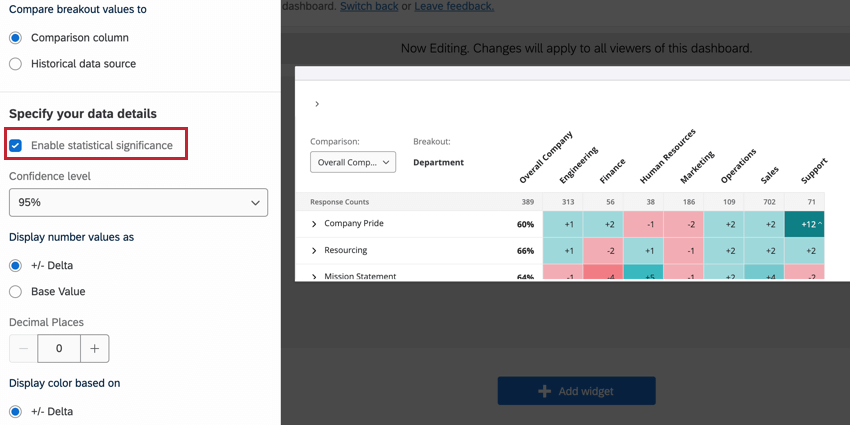
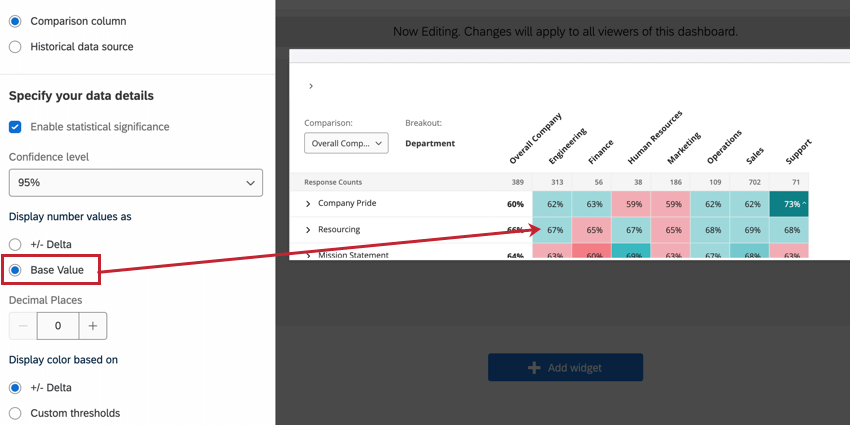
Display number values as
You have 2 options for displaying the number values in your heat map widget:
- +/- Delta displays the difference between the comparison’s value and the breakout’s value of the field.
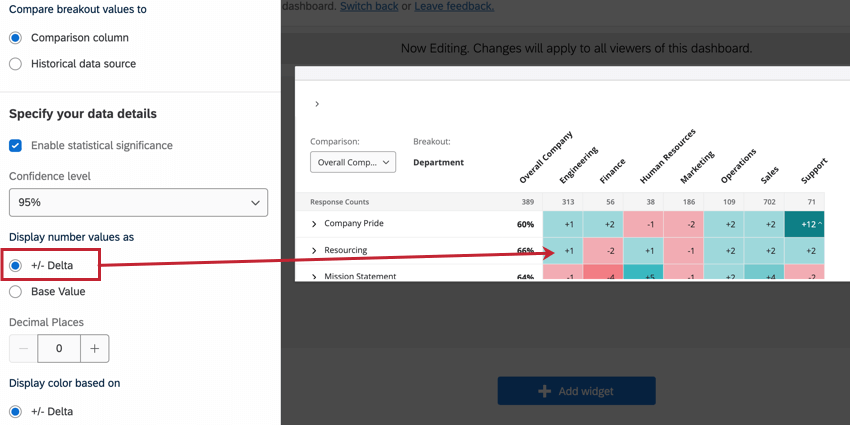
- Base Value displays the percentage of engagement (if your metric is favorability) or mean score (if your metric is average). Instead of difference, we see the flat value of how high or low the score was. Therefore, we compare values by color and by looking at the breakout columns versus the comparison column, instead of the values of the breakout columns being based on the comparison.
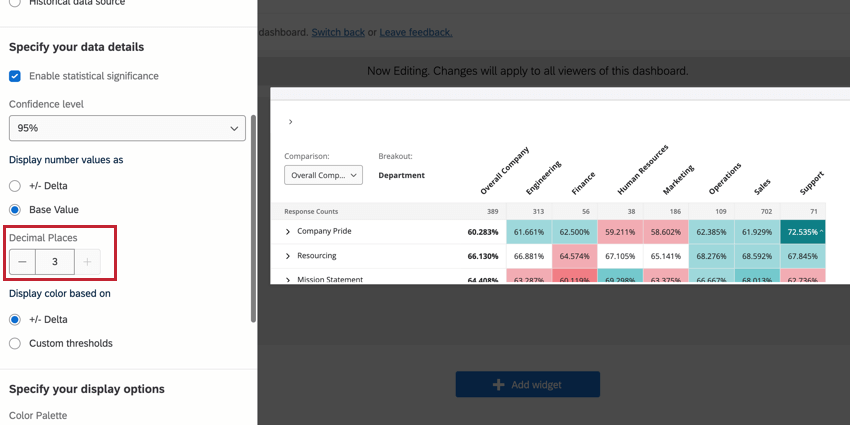
Decimal Places
If desired, you can add decimal places to your heat map values. Use the Decimal Places field to adjust the number of decimal places. You can add up to 3 decimal places in your widget.
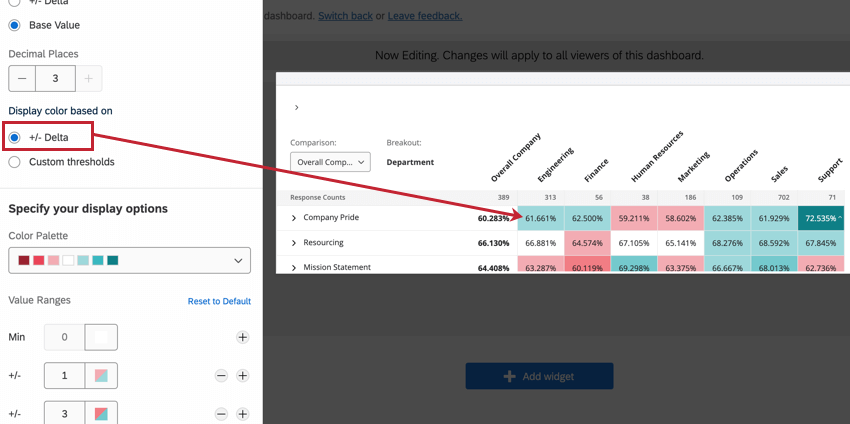
Display color based on
You have 2 options for how the colors in your widget are set:
- +/- Delta: Automatically assigns colors to boxes based on the difference between the comparison’s value and the breakout’s value of the field. The different ranges are automatically set based on your data set values. Usually, delta is the most intuitive way to set a color range scale. See the below section about the widget’s color palette for more information.
- Custom thresholds: Manually assign engagement or average percentage thresholds to assign colors to boxes. See the below section about the widget’s color palette for more information.
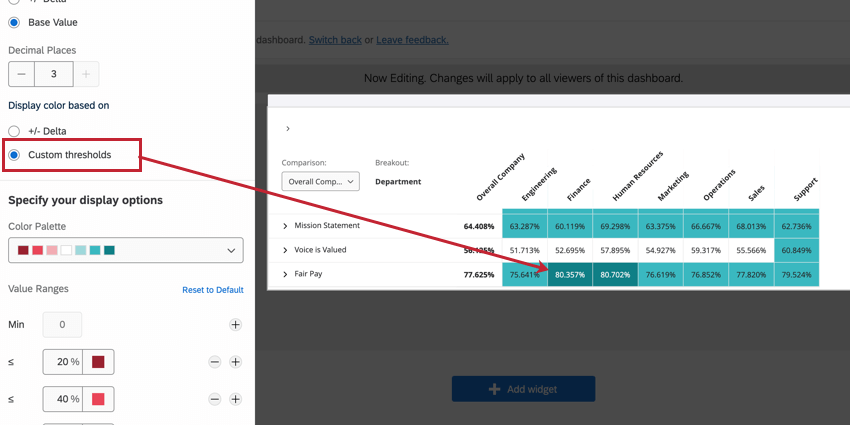
Color Palette
The color palette setting determines the colors that display in the boxes in your heat map widget. The color palettes available are designed by subject matter experts to highlight contrast between high and low values.
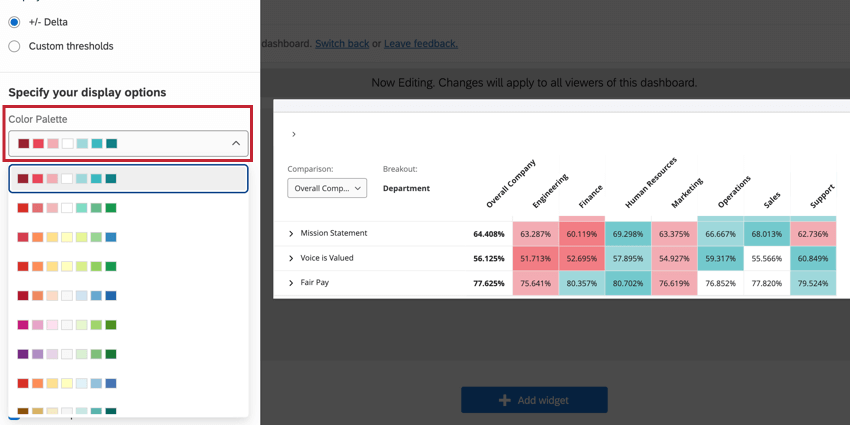
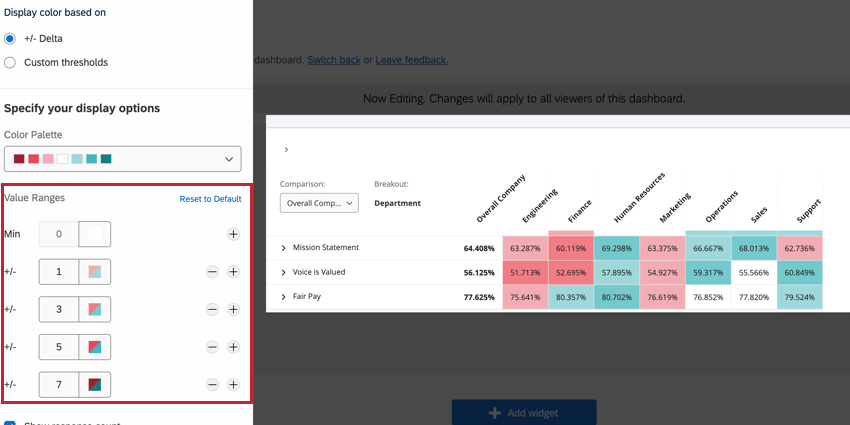
The colors in the value range will be assigned automatically based on the range of values you add. You cannot adjust custom colors for the palette; for example, if you’re using a red and blue palette, you cannot add yellow or purple value ranges.
To adjust the colors for a value range (either delta or custom thresholds), adjust the range values. To add additional range values to your widget, click the plus sign (+). Similarly, remove range values using the minus sign ( – ). Click Reset to Default to revert any changes you’ve made here.
Significance Testing
When displaying comparisons or benchmarks on your widgets, you’ll see a lot of changes from one group to another. But are these changes to be expected, or are they representative of something deeper? How can you decide what changes demand your attention? Thankfully, you can flag whether a difference is statistically significant.
To enable significance testing:
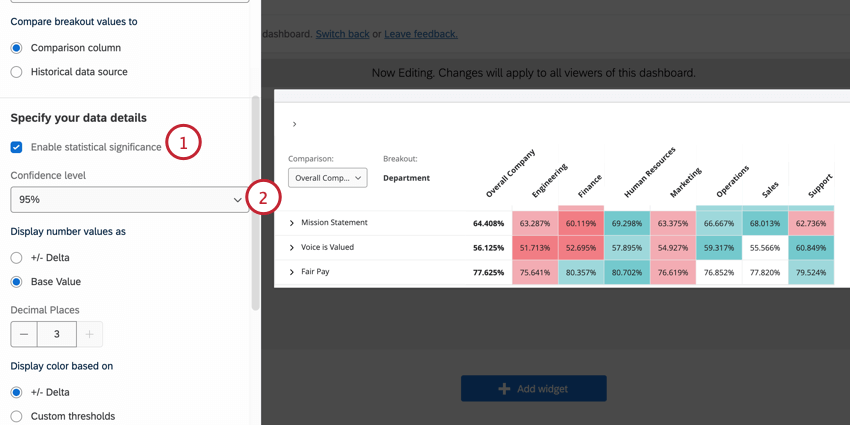
- Select Enable statistical significance.
- Choose your Confidence level.
Types of Significance Tests
The type of significance testing that is being performed varies based on whether you have added a benchmark or a comparison. Significance testing can only be performed if the metric is favorability.
| Favorability | |
| Comparisons | A 2-proportion z-test in 2 tails. Here, we are comparing the proportions of favorability for 2 populations.
Qtip: For statistical tests that are set up with comparisons, the test will be performed with the comparison as it is configured, and will not attempt to remove any overlap between the samples being compared. For example, if your comparison is a subgroup vs. the company overall, the company overall includes the subgroup as well.
|
| Benchmark | One sample test of binomial proportions. Here, we are comparing expected proportion (a benchmark) to the experimental proportion of the binomial question: is this favorable or unfavorable. |
The sample size for categories is the average number of responses across the items in the category.
Understanding Significance in a Widget
The confidence level indicates how confident you would like to be that the results generated through the analysis match the general population. Higher confidence levels raise the threshold for a difference to be considered statistically significant, meaning only the clearest differences will be marked as such.
Once you have enabled significance testing, changes that are significant will have arrows to indicate the direction of the change. Insignificant changes will not have arrows.
Historical Data Comparisons
If you have multiple data sources mapped to your dashboard, you can compare them to each other in your heat map widget. Values will be calculated by comparing the breakout’s score to a historical data source that is mapped to your dashboard.
Your primary data source’s results will be presented first, with the difference in score from historical results in parentheses.
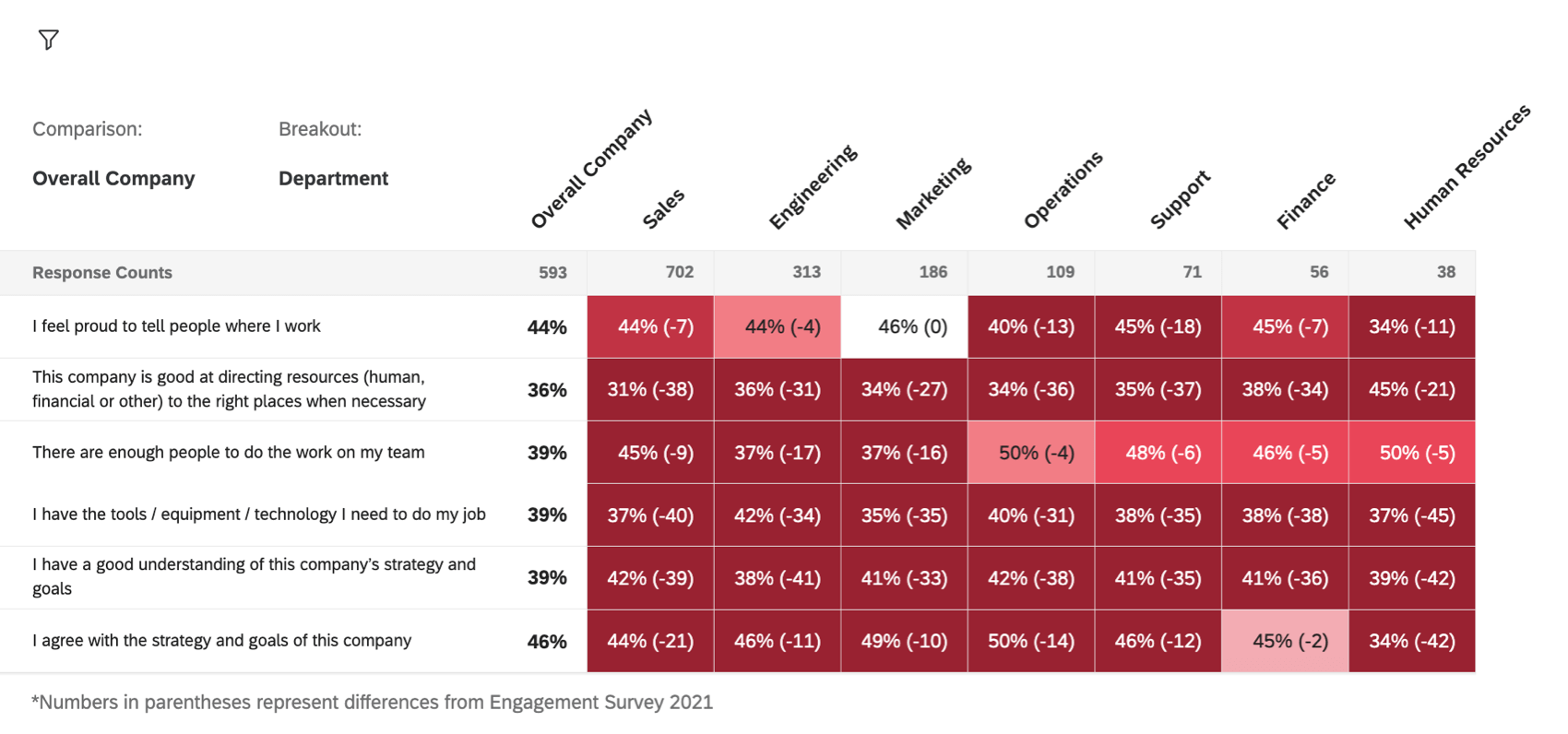
- Make sure a historical data source is mapped to your dashboard.
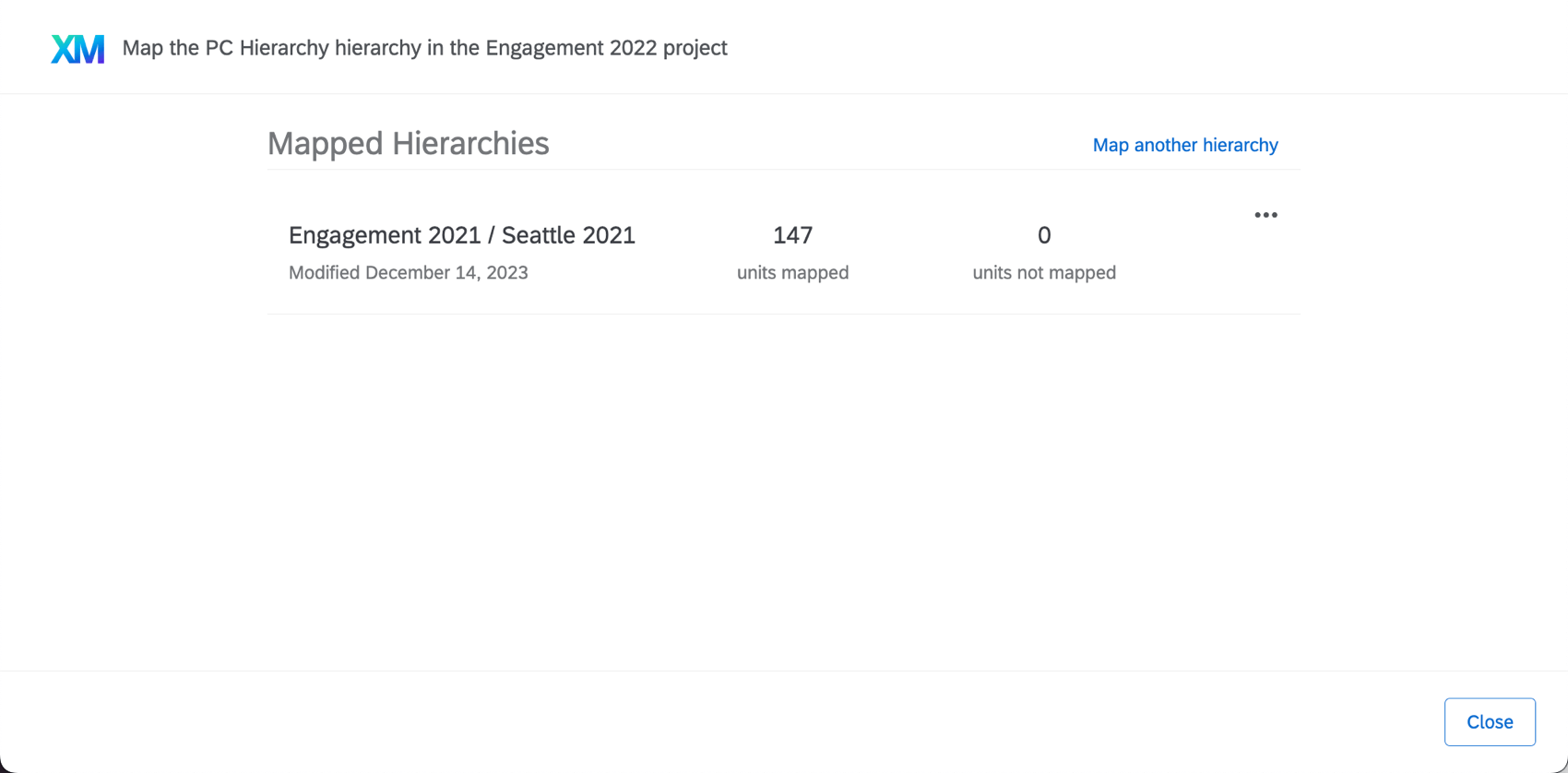 Qtip: Your historical source will need data and to have its hierarchy mapped to your current hierarchy. If you need help with these steps, see Uploading Historical Data.
Qtip: Your historical source will need data and to have its hierarchy mapped to your current hierarchy. If you need help with these steps, see Uploading Historical Data. - Add a filter to your heat map widget.
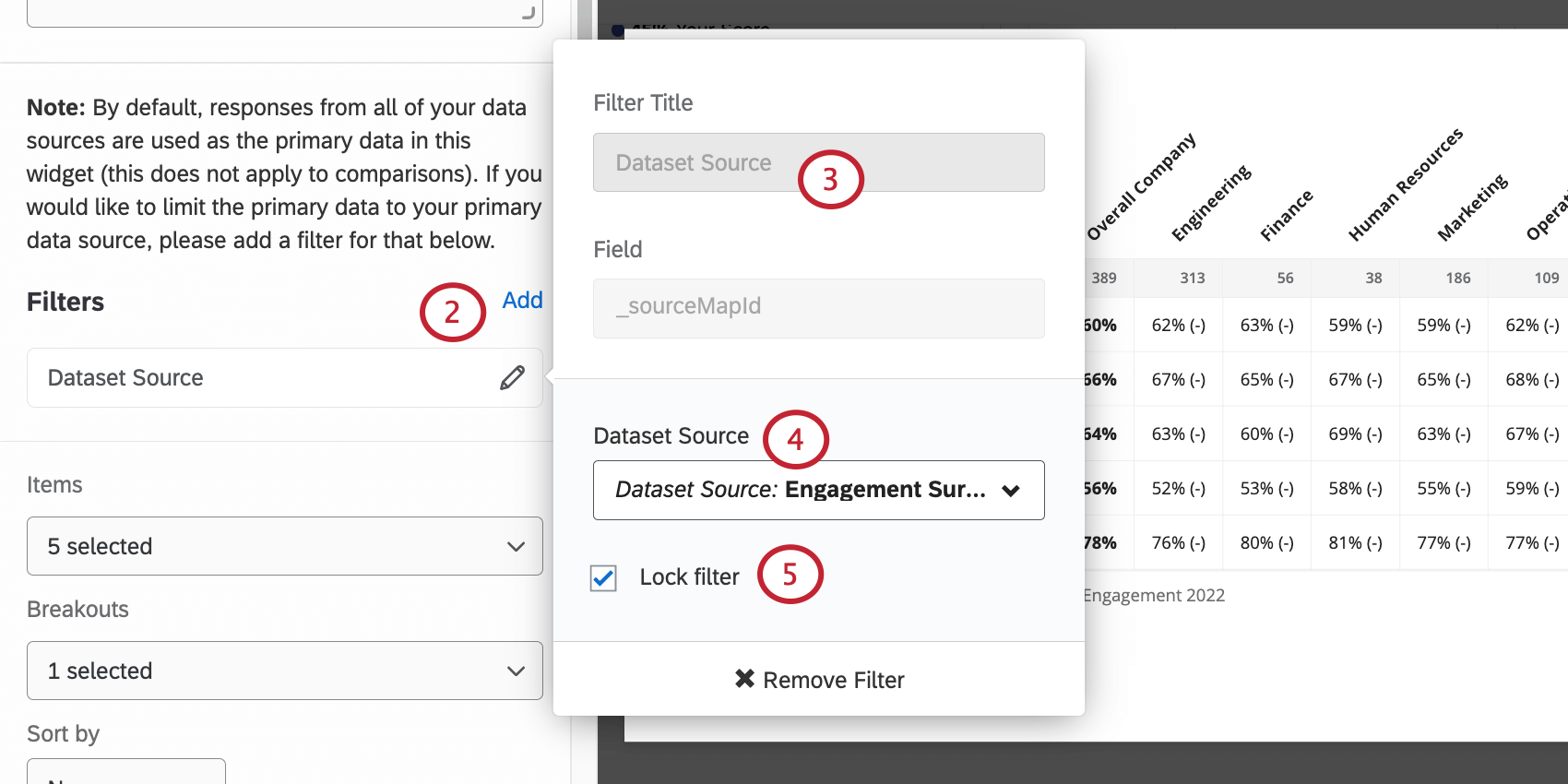
- Select Dataset Source.
- Set the filter equal to the primary data source. This is the more recent engagement survey, where you’ve created this dashboard.
Qtip: If you do not filter for your primary data source, your comparisons will be inaccurate.
- Lock the filter to prevent dashboard viewers from adjusting it.
Attention: Any dataset source filters on a heat map widget will override your dashboard filters. For example, if you filter your widget to compare data from 2022 to 2023 and then filter your dashboard to only show data from 2022, your heat map widget will still compare data from 2022 against 2023.
- Set up your heat map widget.
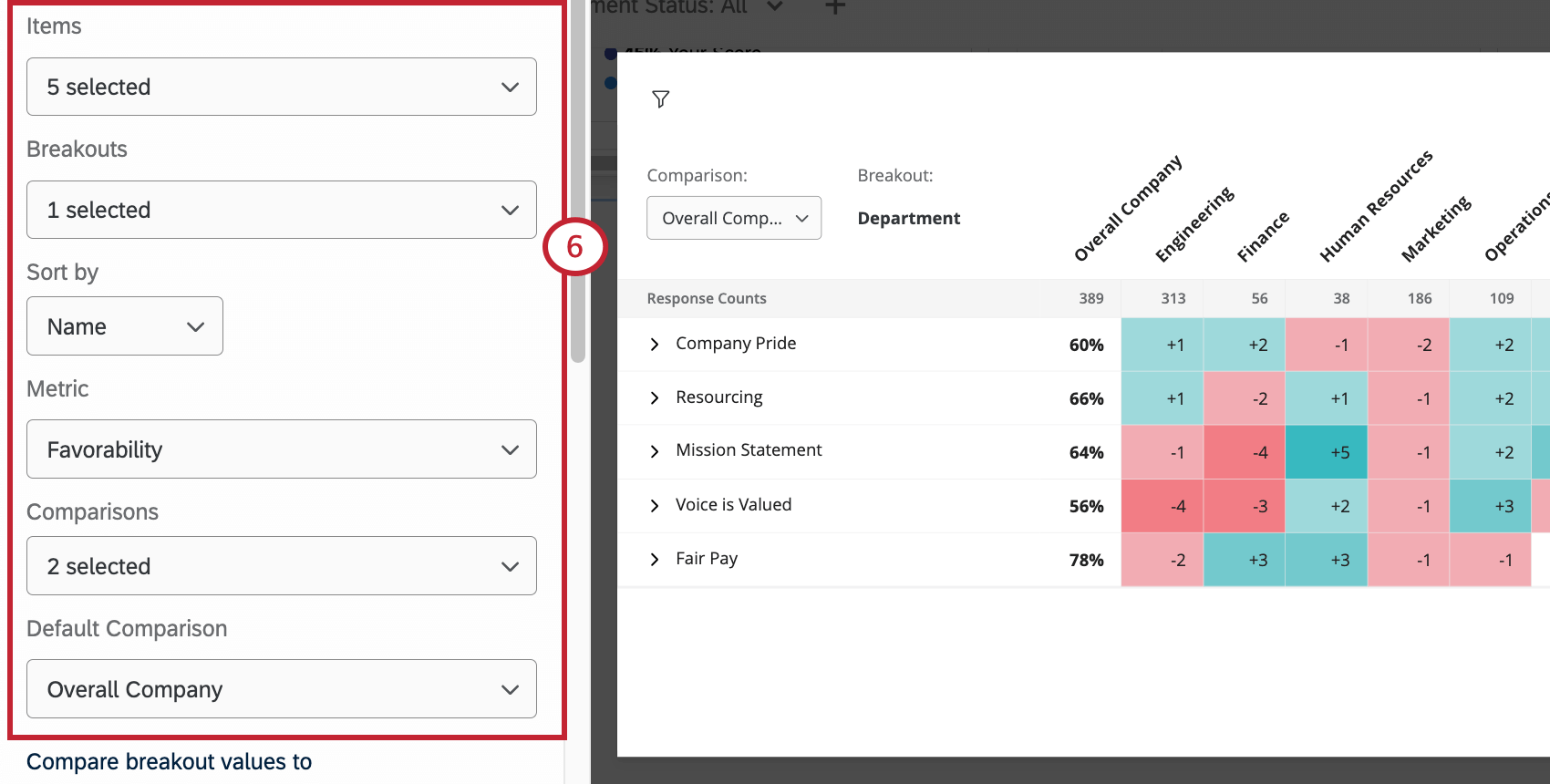
- Under Compare breakout values, select Historical data source.
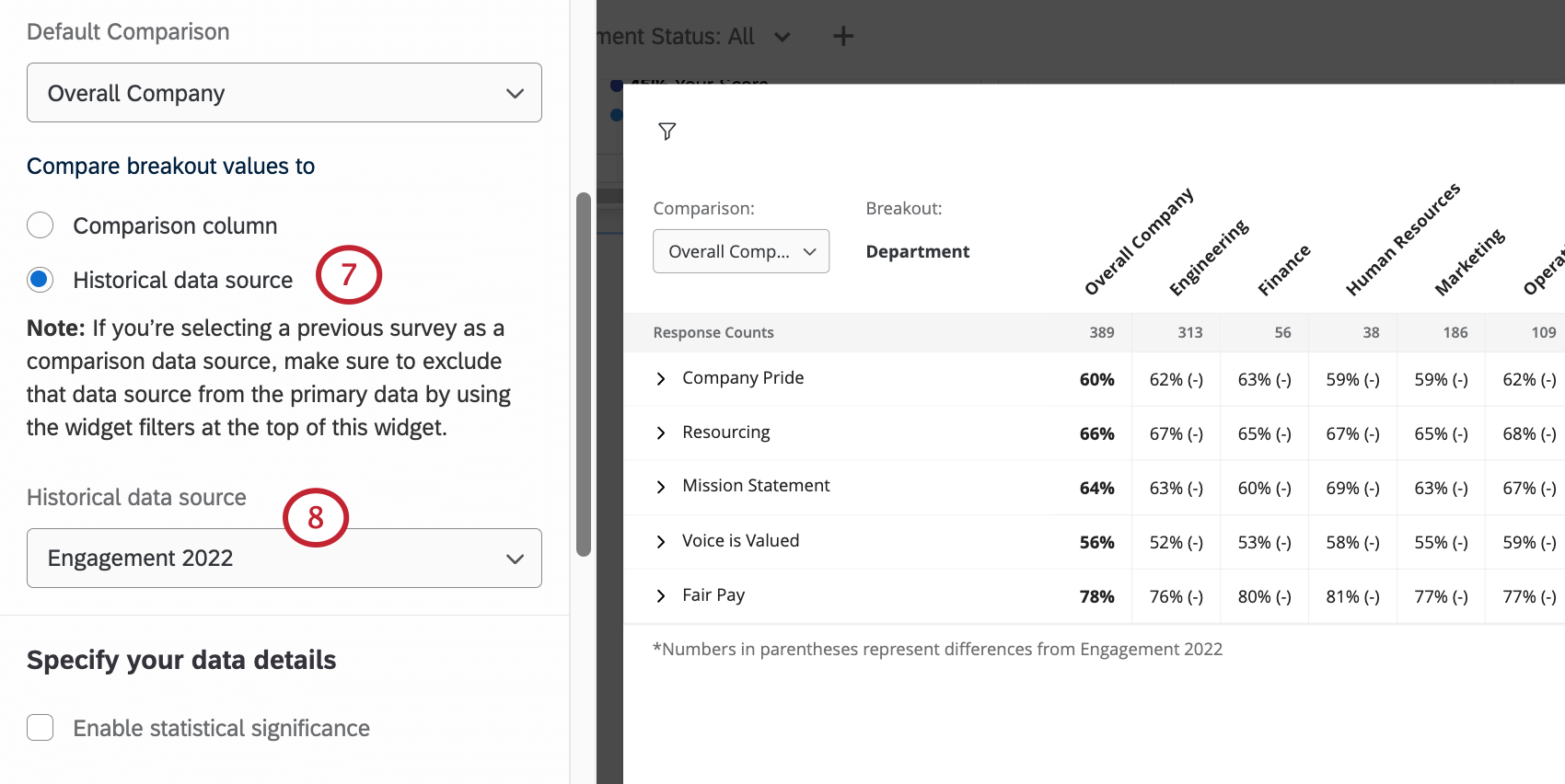
- Under Historical data source, select your secondary dashboard data source.
Additional Customization Options
This section covers additional options you have available for customizing a heat map widget.
Title and Description
Like all widgets, you can add a title and description to a heat map widget. These are useful for telling your dashboard viewers the importance of the data they’re looking at.
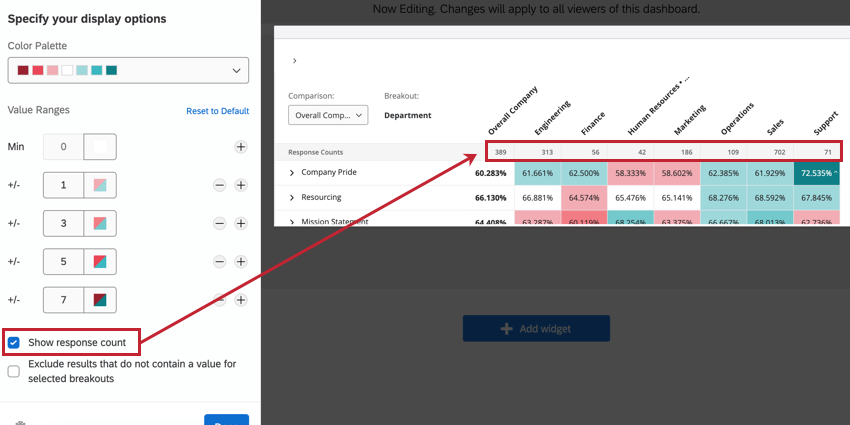
Show response count
Enable Show response count to add a row at the top of your heat map widget that shows the number of responses that are in each column breakout.
Exclude results that do not contain a value for selected breakouts
By default the Exclude results that do not contain a value for selected breakouts option is disabled. When disabled, responses that do not include a value for the selected breakout will be aggregated together into a [No Value] column. If enabled, responses that do not include a value for the selected breakout will be excluded from the widget.![the [no value] column in a heat map widget](https://www.qualtrics.com/m/assets/support/wp-content/uploads//2018/09/heat-map-no-value.png)
Viewing a Heat Map Widget
Heat map widgets can display data in a few different ways. This section will cover how to view a heat map widget as a dashboard viewer so that you can understand the data displayed to you.
Switching Comparisons & Breakouts
If the dashboard builder added multiple breakouts and comparisons to the widget, you can switch the currently displayed breakout and comparison by using the dropdown menus in the top left corner of the widget.
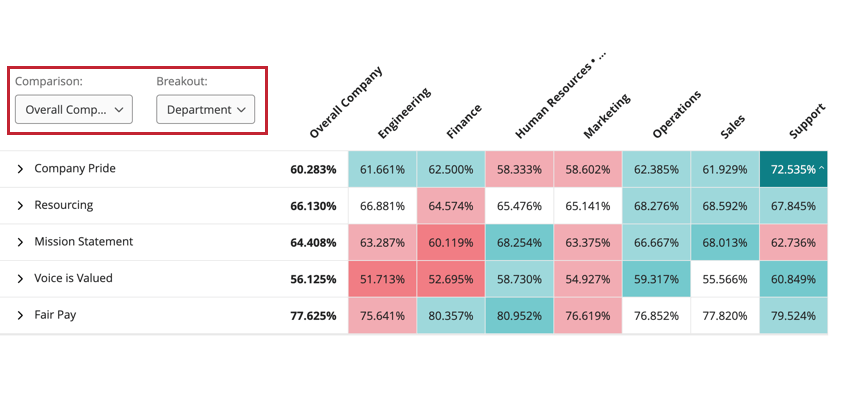
Breakout Comparisons
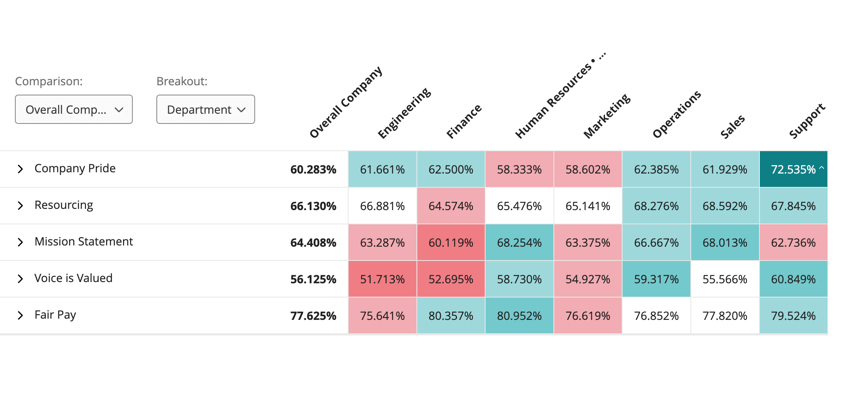
The heat map widget displays data by comparing the values for a question or category by your chosen metadata breakout. When viewing data in a heat map widget, the data in the widget will be different depending on how the dashboard builder decided to compare data:
- Data can be compared against the currently selected comparison. If this is selected, you will see a dropdown for switching comparisons if the dashboard builder added multiple comparisons.
- Data can be compared against historical data. If this is selected, you will see data in parentheses and a message below the widget telling you what data source is being used. You will not see a dropdown menu for switching comparisons.
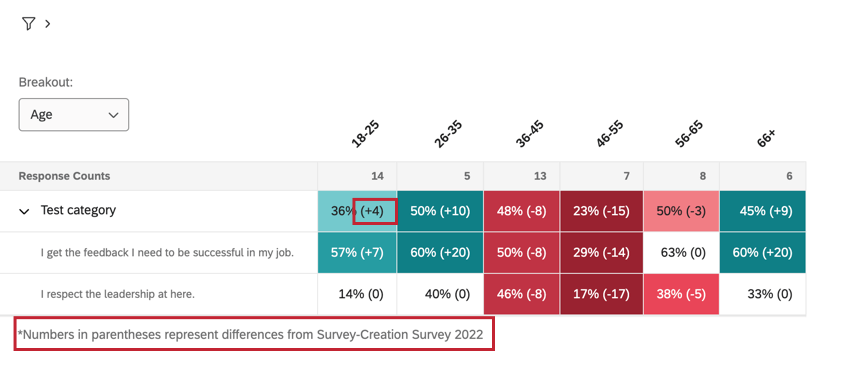
Delta vs Base Value
Depending on the widget’s settings, you may see numbers displayed as a base percentage (e.g., 80%) or as a delta change (e.g., +1). See Display Options for more information about both of these data formats.
Viewing More Information
You can hover your mouse over a statistically significant data point to view more information about that data point. 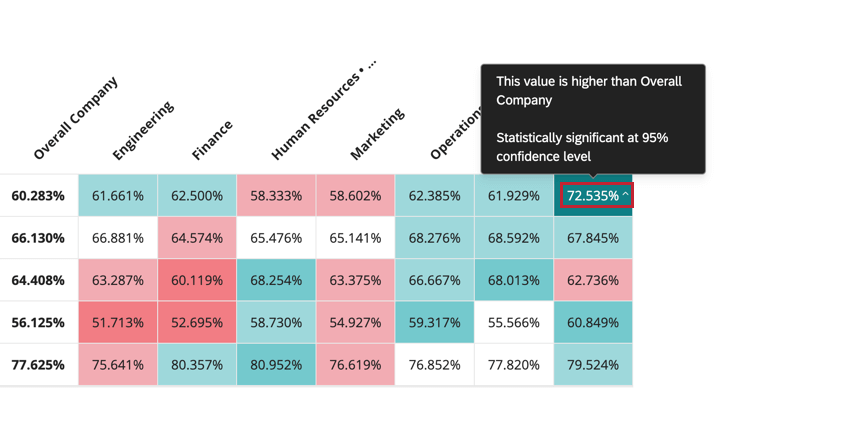
Exporting Data for Heat Map Widgets
If you export a heat map widget with significance testing enabled, information about the statistical significance of your data points will be included in the export.
When exporting the widget to PDF or JPEG, data is exported exactly as it displays within the widget, including colors and arrows to indicate statistical significance. 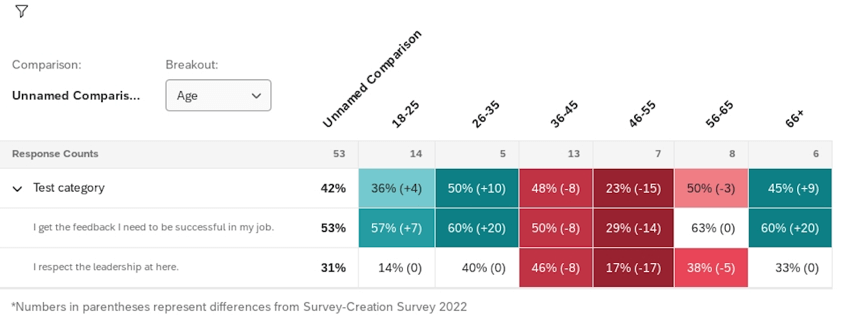
When exporting to CSV, TSV, or XLXS, data is exported in a spreadsheet format that contains all the same information as your widget, including statistical significance. In these exports, multiple (2-3) columns contain the data for each column of your heatmap. These columns include the following data:
- The value for the heat map column.
- The delta change of the value compared to the comparison or historical data source.
- The statistical significance of the data point, if statistical significance is enabled. Statistical significance can be one of the following options: POSITIVE, NEGATIVE, or NO.