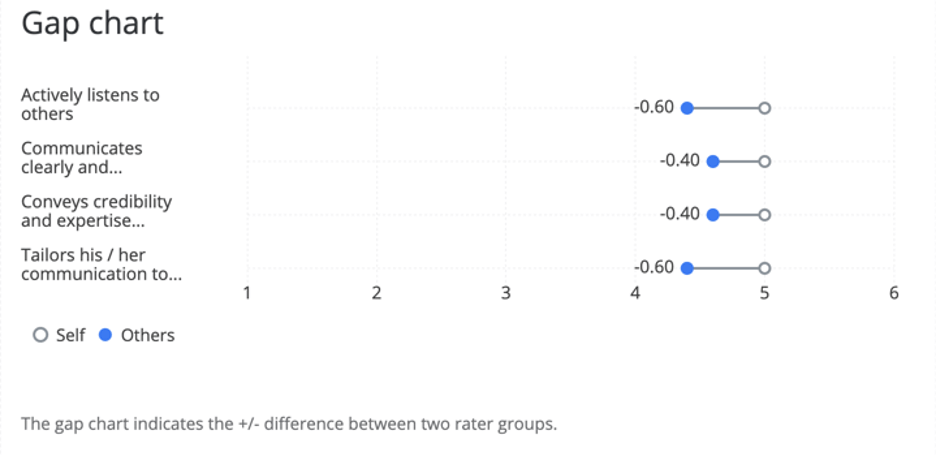Gap Chart (360)
About the Gap Chart
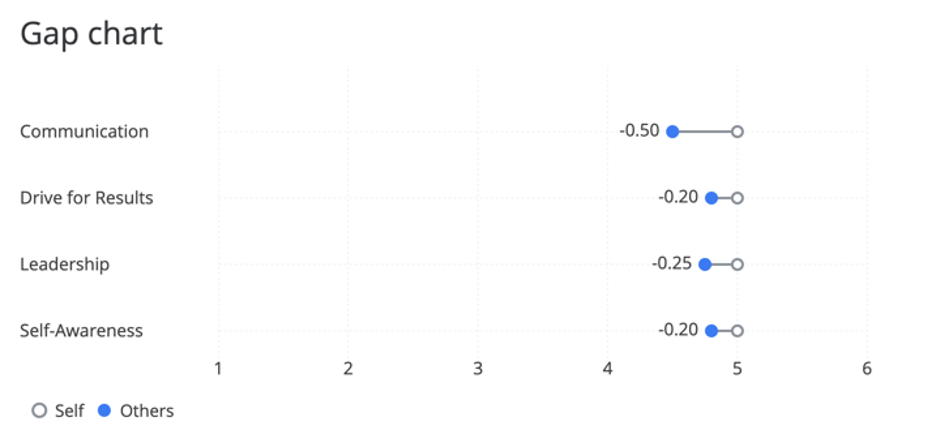
The Gap Chart visualizes the difference, positive or negative, between two rater groups. The x-axis of your chart is average score.
The table automatically compares data from Self and Others, but can display data from any two different rater groups. For example, you can show the gap between how colleagues rate the subject and how their manager does. The gap is calculated by subtracting the results of the second rater group from the first rater group.
Data Source
You must set up scoring categories before you use a gap chart in your report. The gap chart can show data in two different ways:
- See gaps in the specific questions (“items”) in one scoring category.
- See gaps in entire scoring categories.
Comparing Questions in a Scoring Category
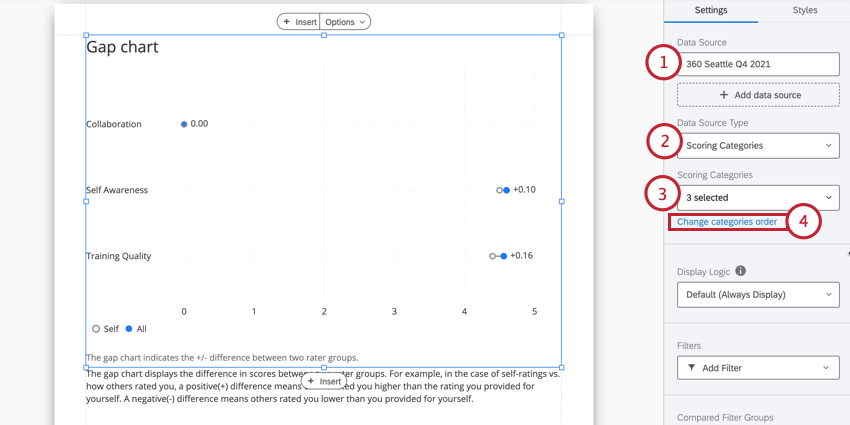
- Under Data Source, choose the project you want to pull data from. By default, this will be the 360 project you created the report in.
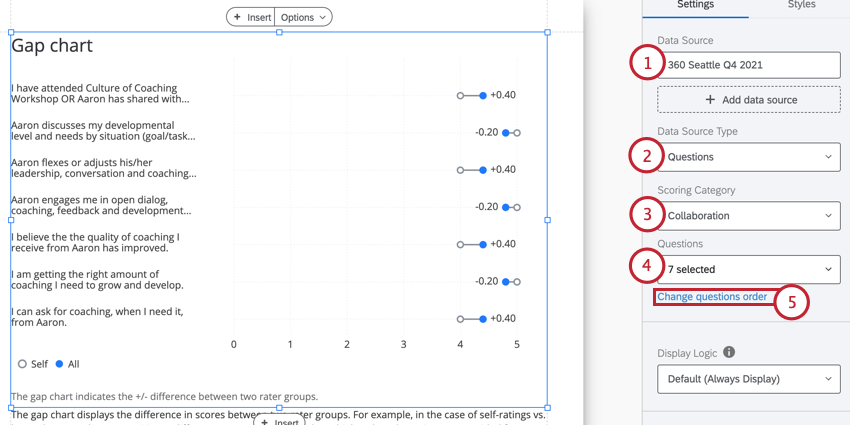
- Under Data Source Type, change your Data Source Type to Questions.
- Under Scoring Category, choose the scoring category you want to display items from. You can only pick one.
- Under Questions, select the items you want to display. Deselect items in this dropdown to hide items you don’t want to include in the chart.
- By default, this visualization will display questions in alphabetical order. You can change the order questions appear in by clicking Change question order.
- Hover your mouse to the left of the question that you want to move. An icon will appear that you can click and drag to rearrange the question in the visualization.
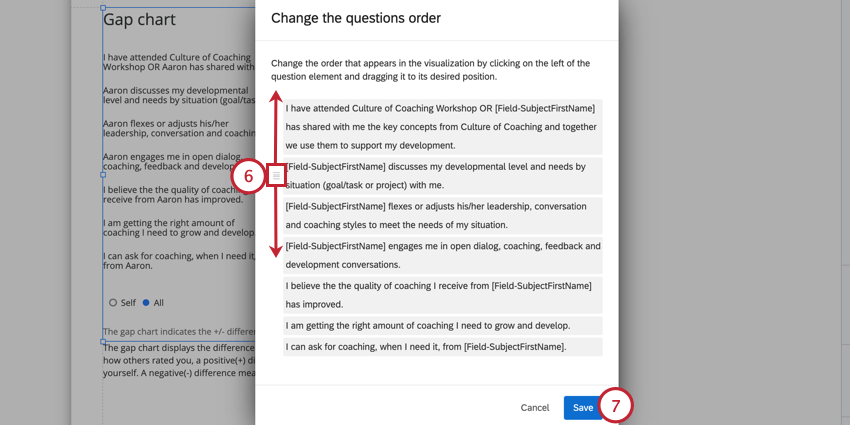
- When finished, click Save.
Comparing Scoring Categories
- Choose the project you want to pull data from. By default, this will be the 360 project you created the report in.
- Change your Data Source Type to Questions.
- Choose the scoring categories you want to display. You can pick as few or as many as you want.
- By default, this visualization will display categories in alphabetical order. You can change the order categories appear in by clicking Change categories order.
- Hover your mouse to the left of the category that you want to move. An icon will appear that you can click and drag to rearrange the category in the visualization.
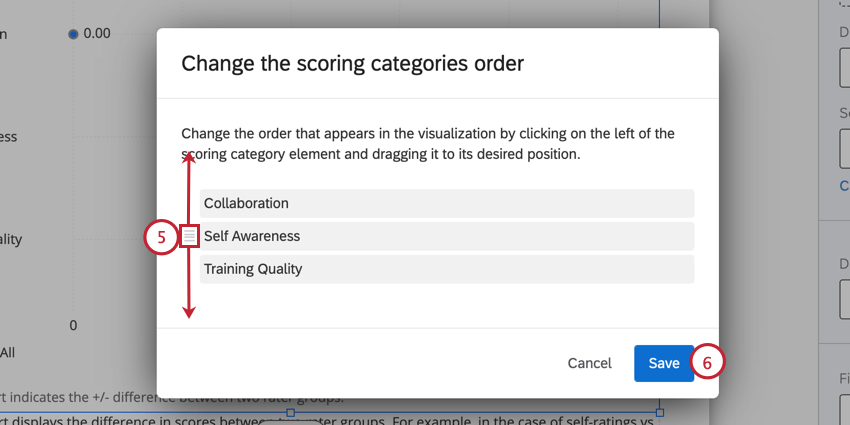
- When finished, click Save.
Display Logic
Display logic is a means of hiding a chart or table if not enough responses have been collected yet. It works the same way in this visualization as it does in all other 360 visualizations. See the linked page for more details.
Filters
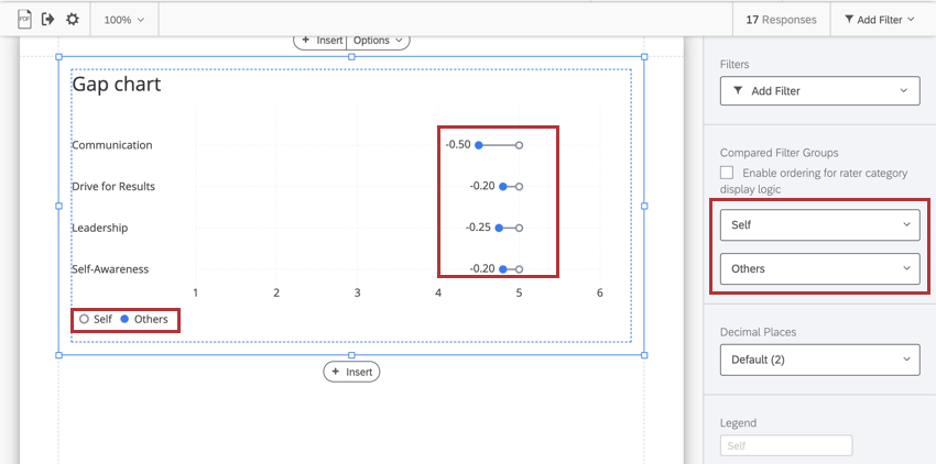
By default, the gap chart doesn’t have a filter attached. However, it is pulling data from “All” evaluations of the subject. This is because you can choose what rater groups you are comparing in the table.
This filter setting can be used to filter the table by other demographics or employee metadata (e.g., a specific office or region), and is not a good use for rater group filters. See 360 Basic Filtering for a guide on more general filtering.
Compared Filter Groups
Use the dropdowns to designate what rater groups should be compared in your table. By default, this is self (how the subject evaluated themselves) vs. others (how others evaluated the subject), but it can be any two filter groups you want.
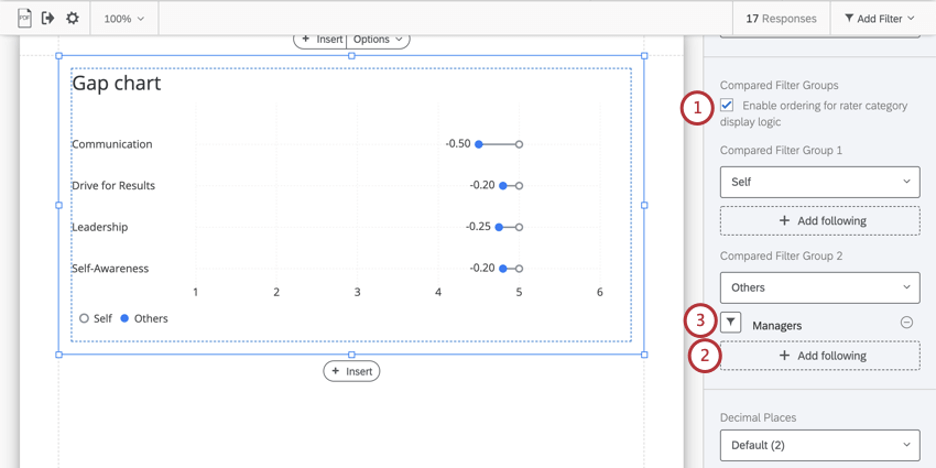
Rater Category Display Logic
Rater category display logic allows you to customize the conditions under which a data source is displayed. For example, you can set logic that allows you to hide or display a data source under specific conditions.
If you have rater category display logic set up in your report, then you can configure your gap chart so that other filter groups are substituted in the event that rate category display logic hides them.
- Select Enable ordering for rater category display logic.
- Underneath the filter group that might be hidden by rater category display logic, click Add following.
- Select the filter group you want to substitute.
To remove substitute filter groups, use the minus sign ( – ) next to its name. You can add multiple substitutes. The table will check them in the order they are listed.
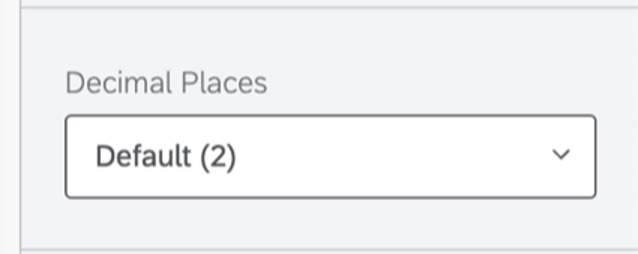
Decimal Places
Adjust the number of decimal places displayed in numbers on the table. Pick from 0 to 5.
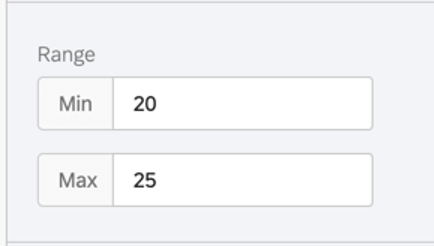
Range
The range will adjust the x-axis of the chart. You can erase the value you’ve entered to allow the chart to automatically set a minimum and maximum value.
Footer
The footer contains the following text, which explains how the agreement chart works so subjects can better understand their reports. Select or deselect the Footer checkbox to either hide or display this footer.
The gap chart indicates the +/- difference between two rater groups.
Styles
Switch to the Styles tab to adjust the margins around the edge of your chart. Switch to Advanced to adjust margins on each side independently of each other.